TOPIC ONE
NATURE AND SCOPE OF MARKETING;OVERVIEW OF MARKETING.
Marketing is the management process responsible for identifying, anticipating and satisfying consumer needs profitably.
It is also the performance of business activities that direct the flow of goods and services from producer or seller to the consumer/buyer.
It is also a social and managerial process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating and exchanging products of value with the others.
Marketing management refers to the overall process of planning, implementing, controlling the marketing program (strategy) and individual marketing functions; appraising the risks and benefits in decision making and focusing on total quality.
Sales/selling on the other hand is the transfer of ownership and possession of goods to the purchasers.
APPLICATION AREAS OF MARKETING.
- Profit making enterprises.
- Government institutions
- Nonprofit making organizations.
ELEMENTS/ENTITIES BEING MARKETED TODAY
- Goods-phones,shoes,soaps,detergents
- Services;hotel,hair dress
- Events-trade shows,world cup, valentine,
- Persons-rudisha, oliech.winfrey.
- Places-city or state.
- Organisations-airtel, safcom,bidco,equity.
- Ideas-this is mainly encountered by many social marketers i.e. don’t drive and drink.
- Experiences –e.g. a trip to Mount Kilimanjaro, lake turkana etc.
- Information-this is usually the knowledge created and disseminated by universities and colleges through teaching and publications mainly in media.
- Properties-mainly real estates as well as financial instruments.
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN SALES AND MARKETING.
Sales and marketing always have had a close relationship, so close that many people have confused the two being the same.
- Marketing is a method of bringing customers to a business as well as making others aware of the business product and brand. Sales is selling the product the company offers.it can be achieved through phone, interaction as well as web page.
- Marketing sells the idea of product and services to everyone whereas sales sells the actual product one on one through personal interaction.
- Marketing generates interest but sales brings in money.
- Marketing does everything it can to reach and persuade prospective buyers while sales does everything it can to close the sale and get assigned an agreement/contract.
- Marketing responsibility is selling the idea while selling has a responsibility of selling the product and can be achieved through sales making.
- Selling is only a part of firm marketing activities and refers to personal communication of information to persuade a prospective buyer to buy something.
- Marketing refers to the process of planning,exchanging,the process,concept/idea,pricing,promotion and distribution of goods and services and ideas to satisfy companies or individuals.sales excludes all this.
- Marketing has led to the emergence of marketing concepts(philosophies that aim at satisfying customer needs) while selling has led to the emergence of selling concepts(a philosophy that encourage organizations to undertake a large scale selling promotion effect.
- Sales people usually sells to customers the products while the marketing meets the organization with customers. the major objectives of sales department is responsible for activities like promotion. marketing ignores all this.
CORE MARKETING CONCEPTS.
- Need-this is a state of felt deprivation most of which is inborn and many can not do without eg need for food,shelter and clothing.
- Want –they are specific satisfaction for particular needs and are insatiable ie one can never fully satisfy them.
- Exchange-this is the act of obtaining a desired product from someone by offering something else in return.
- Product-this is anything that can be offered to someone to satisfy a need or want and can be a good/services(doctors,hair cut),tangible or intangible.
- Demand-This are human wants that are backed by the purchasing power of an individual.
- Customer value-this is the difference between the value the customer gains from owning and using a product and the cost of obtaining the product.
- Customer Satisfaction – this depends on the customers perceived performance in delivering value relative to the buyers expectation.
- Quality-customer satisfaction is closely linked to quality of products and services.many marketers have now adopted Total Quality Management programmes assigned to constantly improve the quality of their offers and marketing processes.TQM can narrowly be defined as freedom from defects.
- Exchange-this is the act of obtaining a desired object from someone by offering something in return.
- Transaction and relationships-this are created mainly through satisfaction of consumers needs and wants.
- Market-the concept of exchange and relationships led to the concept of a market.these buyers share a particular need or want that can be satisfied through exchange relationships.
THE MARKETING PROCESS.
Diagram representing the above concept in a circular flow form-Diagramatic approach.
- Theoretical approach,
1.Understanding the market place and customer needs.this includes;understanding customer needs,wants and demands,market offerings,customer value and satisfaction,exchange relationships and the market.
2.Designing a customer driven marketing strategy.once it fully understands consumers and the market place,marketing management can design a customer driven marketing strategy.the general strategies/generic strategies/competitive forces strategies as proposed by micheal porter are adopted world wide by all marketers namely;
- Cost leadership strategy-this is where a firm incurs the lowest costs in production as opposed to other businesses in the same line of production.
- Differentiation-this involves offering a product that is unique .
- Market Focus/target-this involves targeting the innovators as opposed to laggards in a market.
3.Prepairing an integrated marketing plan and programme-this is where the marketer will outline the consumers and the company that will be served and create value to consumers.next,the marketer develops an integrated marketing mix ie 8 ps of marketing ranging from product,price,place,promotion,people,process,probe and process.
- Ensuring customer relationship management-this is the overall process of building and maintaining profitatble customer relationship by delivering superior customer value satisfaction.this is achieved mainly through;
- Customers perceived value which involves evaluation of the differences between all the benefits and all the costs of a market offering relative to those of competing offers.
- Customer satisfaction:product performance match buyers expectations.
5.Capturing value from customers.this is in return in the form of current and future sales,marketing share and profits.
MARKETING ACTIVITIES.
This is any activity that a business organization undertakes to build brand awareness.they include;
- Product placement in entertainment-video games;holywood where people pay to enjoy this services.
- Trade shows
- Search engine marketing-ranking.
- Newsletters and articles
- Cold calling via phones
- Website design
- Buying
- Selling
- Transportation
- Financing-mostly in sponsorship programs.
- Standardization and grading.
- Advertising
- Branding ,packaging and labeling.
MARKETING GOALS.
- To attract new customers by promising them superior value.
- To keep the current customers by satisfying them accordingly.
- Creating brand awareness.
- Engaging the customers-e.g. the wings to fly program me adopted by equity bank.
- Building positive reputation towards a firm ie.good public relations to the outside world as well as the corporate social responsibility.(C.S.R) as well as customer relationship management(C.R.M).
- To ensure companys growth
- To offer education to the customers
- Talent remittment.
- To ensure profit margins are okay due to the returns on the investments.
- To increase sales volume
- To increase a firms market share.
- To offer quality products.
- To ensure employee welfare.
IMPORTANCE/ROLES OF MARKETING TO THE SOCIETY TODAY.
- Creates utility-this is the ability to satisfy a need ie form utility-this occurs mainly when we have a change in state.place utility-this mainly occurs in transportation.time utility-this arises in all retail outlets and poscession utility-arises when we have ownership of goods.
- Employment creation-this arises when one gets task of designing bill boards,website designers,retailers,wholesalers,warehousing,communications as well as doctors and lawyers indirectly.a good example is in the united states where between ¼ and 1/3 of civilian labour force is engaged in marketing activities and projections indicate that future employment in marketing will remain strong.
- Creates revenue to the government due to the taxes that are levied to the marketers.
- Earns a country foreign exchange mainly through international marketing.
- Entertains consumers e.g. some tv adverts.
- Consumers get informed about products that are prevailing in the markets-people are able to consume what they would not haveconsumed as there is accessibility to products due to cross-border trade,international trade etc.
- Widens the markets-this is mainly through advertisements,salespromotion and distribution.it is also through marketing that goods and services find their way into the trading blocks thereby increasing sales e.g. PTA.COMESA and European markets.
- Helps to develop brand loyalty-this arises due to the repeat purchase by existing customers and favourable accommodators by existing customers to friends,neighbours and others.
- Helps to introduce new products in the market therefore raising the standard ofliving for most people e.g. shopping at internet
- It generates consumers enthusiasim(become interested in something eagerly) for goods and services.
- Has a strong impact on beleifs and lifestyles of people-marketers are criticized as developing materialistic attitudes .
- Helps to improve the quality of life as well as preservation of the environment- marketers encourage firms to make safer products ie low-tar cigarettes,create public messages on energy conservation,cure disaeses(e.g. usage of Dettol),driver safety ie don’t drink and drive,abuse alcohol and other topics.
MARKETING /SALES MANAGERS FUNCTIONS/TASKS/ROLES
- Environmental analysis and marketing research-this usually involves monitoring and adapting to external factors that affect successs or failure such as the economy and competition and collecting data to resolve specific marketing issues.
- Broadening an organizations/individuals scope-this involves deciding on the emphasis to place as well as the approach to take on societal issues and international marketing.
- Consumer analysis-this involves examining and evaluating consumer characteristic needs and purchase processes;and selecting the group(s) of consumers at which to aim marketing efforts.
- Product planning-this includes goods,services,organisations,people,places,and ideas-developing and maintaining products,product assortments(a set o all products and items that a particular seller offers for sale to buyers),product images,brands,packaging and optional features and deleting faltering products.
- Distribution planning-this involves forming relations with distribution intermediaries,physical distribution,inventory management,warehousing,transportation,the allocation of goods and services,wholesailing and retailing.
- Promotion planning-this involves communicating with customers,the general public and others through some form of advertising,public relations,personal seling and or sales promotion.
- Price planning-this involves determining price level and ranges,pricing techniques,terms of purchase,price adjustments and the use of price as a active or passive factor.
- Marketing management-this involve planning,implementing,and controlling the marketing program(stategy) and individual marketing functions;appraising the risks and benefits in decision making;and focusing on total quality.
CHALLENGES FACING TH EMARKETRS TODAY.
- Global economy.
- Changes in technology
- Income gap
- Environmental imperative and social responsibilities
- Aging population
- Later marriages
- More divorce
- Single and smaller families
- Emergence of distinct ethnic consumer groups.
- Proliferation of more varied lifestyles.
- Stringent government policies
- Poor infrastructure.
- Inadequate finances.
HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF MARKETING.
Societies have moved from agriculture and individual self sufficient to an economy built around division of labour and specialization,urbanization and industrialization.it should however be noted that production for individual self sufficiency is not marketing because there is no exchange going on hence exchange or trade laid the foundation of marketing and is the corner stone of marketing.
This is clearly shown by the following orientation stages;
1.THE PRODUCTION ORIENTATION STAGE.
Here,the production process was a simple one with the main emphasis laid on production,which was believed to be in short supply,and the economy was characterized by shortages.little or no attention was devoted to marketing and production processes were very local ie within neighbouring areas.the function of a sales department in an organization was simply to sell the copanys output at a price(this was a period of up to 1930.)
2.SALES ORIENTATION STAGE.
At this stage the small producers began to manufacturer their goods in larger quantities in anticipation of future orders.further division of labour occurred and a type of business developed to help sell the increased output ie intermediaries/middlemen.to facilitate communication and buying and selling,the various interested parties tended to settle near each other hence the formation of trading centers.the main idea at this stage was to sell whatever was produced and this called for heavy/substantial promotional effort to be expended.unfortunately,this was the period that the concepts of selling acquired its bad reputation(this was the age of hard selling ie the period up to 1950).
3.MARKETING ORIENTATION STAGE.
Modern marketing was born with the industrial revolution where there was growth of urban centers and declining rural population resulting in rural-urban migration. The emphasis here was on the growth of manufacturing enterprises because the market demand exceeded the available supply (demand greater than supply)but this has changed and supply has now exceeded demand shifting the emphasis from production to marketing.
The marketers must now embrace the concept of integrated/coordinated marketing management,directed towards the twin goal of customer-orientation and profitable sales volume.emphasis here is on marketing rather than selling.but,how well the companies have embraced the marketing is still questionable.
4.SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY AND HUMAN ORIENTATION STAGE.
The conditions of the 1970s led to this fourth stage,which was characterized by the concern for the society.the emphasis here is on social responsibility on the part of the marketers for their survival in the industries.marketers must therefore be concerned with creating and delivering a better quality of life rather than only a material standard of living. The rise in social responsibility as a concept for business was highly influenced by the rise in consumerism movement.
CONCEPTS OF MARKETING/MARKETING PHILOSOPHIES/MARKETING PRINCIPLES.
Marketing concept-this refers to the ways of business thinking that have evolved over time and they include;
- Production concept-this is the oldest philosophy that has guided the sellers.it can be traced to the industrial revolution. Organizations produced in large quantities the belief being that consumers will favor products that are either available or were affordable. Manufacturers therefore focused on improving production and distribution efficiency. This philosophy is applicable when the following conditions exists.
- When demand for a product exceeds the supply.
- When the price of a product is too high and can only be brought down with increased productivity.
- Product concept-this was a belief system adopted by business men before 1920.the belief was that consumers will favour products that offer the most quality(design ) performance and features to them. If u design a product in a way that looks attractive,consumers will have to buy the product.
- Selling and sales concept/”hard sell”.this belief was developed between 1925-1950 and was commonly referred to as hard sell concept(companies using adverts to become the best ie out do the others)and it prescribes that consumers will not buy enough of organisations products unless it undertakes a lot of selling and promotional effort.organisations must therefore advertise their products and employ sales persons to communicate with consumers with the aim of convincing them to buy the products.this theory is applicable for unsought goods i.e insurance,microwave etc.ie it aims at informing,communicating and promoting a companys product.
- Marketing concept.-this is a business philosophy that was adopted after 1950 and the philosophy holds that achievement of business goals depends on determining the needs of customers and delivering the desired level of satisfaction to consumers more effectively and efficiently than the competitors.the marketing concept stands on the following pillars/highlights/considerations.
- Market focus/targeting-the firm must concentrate on one or a few key segments of the market and satisfy their needs.ie marketers usualy target the innovators as opposed to laggards in a market.
- Customer orientation-the firm must carefully define customer needs from the customers point of view.this is important because a satisfied customer:
- Will buy the product again.
- Will talk favourably to others about the firms product.
- Will pay less attention to competing brands in the market.
- Is likely to buy other products that the company may add to its line.
- integrated marketing-this means that the various marketing functions must pull together inorder to satisfy the customer e.g. well trained and motivated employees,good and efficient suppliers e.t.c.
- profitability-the job of a marketer is to satisfy consumer needs at a profit.
5.Societal marketing concept/human orientation concept/social responsibility concept/survival stage/holistic.
This concept is based on detrmining the needs and wants of consumers and delivering superior value in a way that maintains or improves consumers and societies well being.it requires that organisations should not only satisfy consumer needs but act in a way that preserves the welfare of consumer and society.The triangle below illustrates how all stakeholders should be involved in any marketing activity.
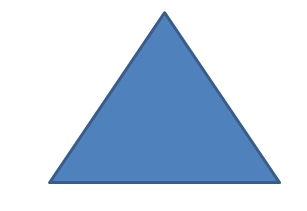
a-balance the society(human welfare).
b-balance consumers(satisfaction).
c-balance company(profits).
BUSINESS RESPONSIBILITIES TO CONSUMERS AND THE COMMUNITY.
- No pollution to the environment.
- Be socially responsible .
- Offer products of right quality.
- Offer products of right quantity.
- Offer products of right price.
- Locate markets and factories at proper places(not within residential areas but convenient to consumers).
- Honouring contracts and following honest trade practices and avoid bribery/short cuts.
- Providing after sale services.
- Achieving better public relations by providing education to the community.
- Ensuring products are safe and well designed.
- Ensuring proper weight measures.
BUSINESS RESPONSIBILITIES TO THE EMPLOYEES.
- To pay fair wages and salaries and in good time.
- Ensuring fair training and promotion of employees.
- Ensuring satisfactory working conditions and social security measures(retirement benefits).
- Ensure good human relations ie maintain industrial peace.
- Provision of freedom,self respect and empower employee.
- Ensuring increase in productivity and efficiency by recognizing merits of employees and giving them incentives.
BUSINESS RESPONSIBILITIES TO SHAREHOLDERS AND OTHER BUSINESSES.
- Pay dividends to shareholders.
- Sensitize shareholders on the need to plough back profits and growth and expansion of business.
- Ensure fairness in relation with competition based on the rule of ethics(avoid unfairness ie low/high cost).
- Ensure professional practices(body rules) in day to day activities of business.
- Practice ethical marketing.
BUSINESS RESPONSIBLITIES TO STATE/GOVERNMENT.
- Maintain impartiality towards political affairs.
- Observing the laws of land.
- Paying taxes and rates.
- Contributing towards good economic conditions of the country.
- Safeguarding against illegal business practices e.g. selling black market goods.
- Ensuring fair play to all the participants of the economy ie employees,shareholders,creditors and customers.
- Ensure maximum production according to the priorities of various sectors laid down by the government i.e quota system.
- Avoid over exploitation of limited natural resources.
SOCIAL CRITISM OF MARKETING.
Impact on individual consumers-this arises due to;
- High prices due to;high costs of distribution,high advertisement and promotion costs and excessive markups.
- Deceptive practices;ie deceptivive pricing,deceptive promotion and deceptive packaging.
- High pressure selling tactics being adopted by companies.
- Shoddy/unsafe products being offered.
- Offering products with planned obsolescence.
- Poor services to the disadvantaged consumers ie left handed and those on wheel chairs.
- Impact on society as a whole-this is mainly encountered in this areas.
- False wants and too much materialism.
- Too few social goods such as sewerage services which are rarely marketed.
- Cultural pollution-some adverts erode the norms taboos and values of customers.
- Too much political power.
- Impact on other businesses-
- Acquisition of competitors.
- Marketing practices that create barriers to entry
- Unfair competitive marketing practices.
TOPICTWO
MARKETINGINFORMATIONSYSTEMS.
The marketing environment is changing at a very fast rate hence there is need for real time and up to date market information. In today’s information based society, companies with superior information enjoy a competitive advantage.
MKIS- is a system that consists of people equipment and procedures that are used to gather, sort, analyse,evaluate and distribute needed timely and accurate information to marketing decision makers.it helps managers to analyse,plan,implement and control various activities in the organization.
ROLE OF MARKETING INFORMATION SYSTEM/EXPALAIN THE BENEFITS A FIRM SHOULD DERIVE FROM HAVING EFFICIENT MARKETING INFORMATION SYSTEM.
- Access information needs-a good mkis should balance the information that managers require against what they really need and what is viable to offer given the organizations resources.ie how much information is needed, cost of obtaining the information given organization resources and benefits of having the information.
- Developing needed information-this involves gathering information as many sources as possible
- Carrying out information analysis-this involves using statistical and mathematical models to analyze information collected and its interpretation
- Distributing the information-the mkis distributes information to various decision
COMPONENTS OF MARKETING INFORMATION SYSTEM.
- INTERNAL RECORD SYSTEM.
This consists of information gathered from sources within the company which helps to evaluate the marketing performance and identity marketing problems and opportunities. The records include;
- Profit and loss statement.
- Balance sheet.
- Sales record
- Employee record.
- Cash flow statement.
This information is used for;
- Day to day planning implementation and control.
- To evaluate the performance of a company.
- To detect problems.
- To create new marketing opportunities and ideas.
- MARKETING INTELLIGENCE SYSTEM.
This is a set of procedures and sources used by managers to obtain every day information about development in marketing environment. Sources of marketing intelligence include;
- Reading books and newspapers
- Trade publications
- Meeting with other company managers.
- Exhibitions and conferences.
- Sales persons.
STEPS USED TO IMPROVE QUALITY OF MARKETING INTELLIGENCE.
- Training and motivating the sales force to identify and report new developments.
- Motivating retailers and distributors to report important intelligence.
- Monitoring competitors activities
- Setting up a customer’s advisory panel made up of representative customers or the company’s largest customers so that a company can gain valuable information about customer needs and feelings.
- Purchasing information from outside suppliers ie research firms outside the company eg synovate.
- Establish a marketing information centre to collect and circulate marketing intelligence.
3)MARKETING RESEARCH.
This is the systematic design, collection, analysis and reporting of data and findings relevant to a specific marketing situation facing the company. There is a design of an interview guide and a questionnaire. Marketing research is based on specific and opportunities that the company would like to pursue. It therefore requires;
- A market survey.
- Product preference tests –why; improvements etc
- Sales forecasts based on various regions
- Advertising evaluation-ie are you effective?.
SOURCES OF INFORMATION.
- Primary sources-this is fresh research ie information being collected for the first time to solve a particular problem or gain insight into a particular event. This information is collected through questionnaires,interviews,observation,fieldsurveys,opinioncalls,experimentation,aptitude tests etc.
- Secondary sources-this is information stored in some records and hence it is not an original information source. It can either be from internal or external sources.
- Internal sources-these are sources of information that already exists within the organization. The information could have been collected for other uses but can be used for the current research eg company magazine and the internal records system.
- External sources-they are sources outside the organization and include the: internet, ministry of trade and industry newspaper, libraries etc.
DATA COLLECTION METHODS.
- Primary data-this is the information at hand and collected for the first time.
- Secondary data-this is data available or gathered(collected and analyzed by someone else; published materials,reports,journals and books
METHODS OF PRIMARY DATA COLLECTION.
- Observation-it is commonly used in behavioral sciences. It is gathering of primary data by investigators own direct observation of relevant people, actions and situations without asking from the respondent. E.g. observing numerous plates containing uneaten proportions of the same menu item indicates that the food is not satisfactory.
Types of observation.
- Structured observation-for descriptive research.
- Unstructured observation-for exploratory research.
- Participant observation.
- Non-participant observation
- Disguised observation.
Limitations.
- Feelings, beliefs and attitudes that motivate buying behavior and infrequent behavior can t be observed.
- Expensive method.
- Survey method-this is an approach most suited for gathering descriptive information. The major types are;
- Structured survey-uses formal lists of questions asked of all respondents in the same way.
- Unstructured survey-the interviewer probe respondents and guide the interview according to their answers.
Advantages.
- Can be used to collect many different kinds of
- Quick and low cost as compared to observation and experimentation.
Limitations.
- Respondent’s reluctance to answer questions asked by unknown interviewers about things they consider private.
- Busy people may not want to take the time.
- May try to help by giving pleasant answers.
- Unable to answer because they can’t remember or never gave a thought to what they do and why.
- Respondents may answer in order to look smart and well informed.
- Mailed questionnaires.
Advantages.
- Can be used to collect large information at a low cost per respondent.
- Respondents may give more honest answers to personal questions on a mailed questionnaire.
- No interviewer is involved to bias the respondent answers.
- Convenient for respondents who can answer when they have time.
- It’s a good way to reach people who often travel.
Limitations.
- Not flexible.
- Takes longer to complete than telephone /personal interview.
- Response rate is often very low.
- Researcher has no control over who answers.
Merits.
- It’s a quick method.
- It’s more flexible as the interviewer can explain questions not understood by respondents.
- Depending on respondents answer they can skip some questions and probe more on others.
- Allows greater sample control.
- Response rate tends to be higher than mail.
- Cheap as it does not include travelling expenses.
Drawbacks.
- Cost per respondent is higher.
- Some people may not want to discuss personal questions with the interviewer.
- Interviewer manner of speaking may affect the respondent’s answers.
- Different interviewers may interpret and record response in a variety of ways.
- Under time pressure, data may be entered without actually interviewing.
This consists of a set of questions presented to a respondent for answers. The respondents read the questions, interpret what is expected and then write down answers themselves. There are three basic types of questionnaires ie
- Closed ended-one chooses among a criterion given.
- Open ended –one is allowed to answer in own words; no boxes to tick are available.
- Combination of both-begins with a series of closed ended questions with boxes to tick and finishes with a section of open ended questions.
Advantages.
- Can be used to reach many people.
- Saves time especially where they have been mailed to respondents
- Cost effective given that be mailed and one can avoid using the interviewer.
- Questions are standardized and therefore responses are likely to be the same.
- Interviewer bias can be avoided when questionnaires are mailed.
- They give a greater feeling of being anonymous and therefore encourage open responses to sensitive questions.
- Effective in reaching distant locations where it is not practical to go there.
Disadvantages.
- Questionnaires mailed to respondents may not be returned.
- The inability to control the context of questions being answered and specifically the presence of other people who may fill the questionnaire.
- A certain number of potential respondents particularly the least educated may be unable to respond to written questionnaires because of illiteracy and other difficulties in reading.
- Written questionnaires do not allow the researchers to correct misunderstanding or answer questions respondents may have.
- Some questionnaires may be returned half filled or answered.
RESEAECH DESIGNS.
- Exploratory research design.
This is the most appropriate when there is little or nothing known about a phenomena of study and there is need to gain insight and ideas about a problem eg customer surveys to find out customer tastes and preferences.
- Descriptive research design.
This is most appropriate where the researcher is fairly knowledgeable about a key aspect/subject of study but has little knowledge if any regarding their characteristic nature of details; hence a descriptive study helps to generate knowledge about the qualitative and quantitative elements of what is being studied.
- Causal research design.
This is concerned with determining a cause and effect relationships and it involves manipulating one or more variables in order to determine their effects eg manipulating price to determine its effect on sales of a company.
STEPS INVOLVED INMARKETING RESEARCH.
- Definition and identification of research problem.
The research problem must be identified clearly and precisely ie it must not be ambiguous (contradictory).
- Determination of the sources of information.
It includes both primary and secondary data sources.
- Determination of data collection methods.
For primary research, interviews and questionnaires can be used while for secondary research, desk research (stored records usually browsed)is used.
- Determination of sample design to be used.
This refers to the group of people/objects that the researcher will make generalization based on the findings. The concern of the researcher is:
- To define the population of interest ie All those people likely to be interested in buying the company’s products.
- Specifying the sampling frame. This is a list of those in the population of interest ie same gender, same income etc.
- Specifying the sampling units ie the type of people to be interviewed or the specific group of people ie eastern, western or coastal regions.
- Selection of the sampling method to be used ie simple, stratified, systematic etc.
- Determination of the sample size. The size must be representative of the total population.
- Data collection.
This involves conducting desk research, field work or experiments. The researcher should ensure that proper data collection instruments are put in place in order to obtain the right information.
- Data analysis and interpretation.
The purpose of data analysis is to obtain meaning from the research carried out. It involves the use of statistical methods and tools eg mean, measures of central tendency and software eg excel as well as hardware’s eg printers to analyze and interpret data.
- Reporting the results.
This involves presenting the findings inform of a report in order for users to make decisions that are relevant to their departments. The report is the yardstick for evaluating the research project.
A GOOD RESEARCH SHOULD SATISFY THE FOLLOWING CONDITIONS.
- Completeness-it should not leave out important details or procedures of the research.
- Accuracy-it should report the exact findings of the research without exaggeration.
- Clarity-should be clear in terms of sentences, expressions and explanations used.
- Conciseness-the research report should be brief and should not elaborate on unnecessary details or be repetitive.
- Simplicity
- Future oriented-focus on long term goals as opposed to short term goals.
- Time bound
- Economical in terms of cost.
- Utilize the principles of the scientific (step by step) method wherever possible.
- Creativity ie think “outside the box”.
- Should follow the ethics of the society.
- Realistic –achievable and measurable.
THE ROLE OF RESEARCH INFORMATION IN MARKETING.
- It provides accurate, effective and useful information that is vital for decision making across the entire organization. The decisions include;
- Size of the market.
- Customers and their buying motives.
- Changing trends in the market.
- Customer satisfaction /dissatisfaction with a product.
- It can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of the various elements of the marketing mix such as advertising.
- It provides feedback to the organization which helps it compare performance before the marketing strategy was put in place and after.
4).MARKETING DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM.
This is the systematic collection of data from the other three systems, the use of tools and techniques with supporting software and hardware by which an organization gathers and interprets relevant information and turns it into a basis for making marketing decisions. The decisions can be classified as;
- Strategic decisions
This are made by top level management and involves establishing objectives for the organization and long term plans for attaining those objectives.
- Tactical decisions.
This are made by middle level management and are concerned with allocation of resources needed to meet organizational objectives.
- Operational decisions
They are made by lower level management and involve executing specific tasks.
TOPIC THREE
MARKETING MIX.
This is a framework which helps to structure the approach to each market. The mix is a bundle of variables offered to the customer. This is a tactical/operational part of a marketing plan.it is composed of the elements below
- Product -refers to anything that can be offered to a market for attention, use, or consumption that might satisfy a want or need
- Price- This is the amount of money charged for a good or service.This is the sum of value consumers exchange for the benefit of having or using a good or service.
- Place- refers to channel of distribution or the route or path followed by a product as it moves from the producer to the consumer/final user.
- Promotion- Promotion is a function of marketing mix and is a technique used in creating awareness on the companys product as well as the company itself.
- Process-involves taking into account all elements that translate to satisfaction of customer needs and wants.
- People-this are the living creatures who are willing and able to transact.
- Physical evidence-this are elements that can be seen,felt,heard or smelt.
- Probe-this basically refers to asking questions or carrying out a market research.
FACTORS AFFECTING MARKETING MIX ELEMENTS.
- Finance-the business should consider how much money is to be spent on marketing.
- Needs of the market-the business should continue to carry out market research as the business grows,as the needs of customers change over time.
- Competitors-marketing mix can be used as a response of competitors actions in the market
- Technology-the business may change where goods are bought and sold according to changes in technology e.g. internet.
- Demand of products-affected by price element as they are inversely related.
- Nature of the product-affected by the form or physical evidence.
IMPORTANCE OF MARKETING MIX ELEMENTS.
Generally, the specific individual marketing mix elements can be used to elaborate more on the specific marketing mix importance’s.
- Offerings in the market
- Helps to target the specific individual groups in the country.
- Assists in message delivery
- Value creation to customers.
TOPIC FOUR.
MARKETING ENVIRONMENT.
The environment can be defined as all the circumstances,people,things and events around all the marketing activities. A business performance is often dependendant on how the enterprise influences and is influenced by its environment.The environment is mainly classified into two main forms;
- INTERNAL /MICRO/CONTROLLABLE/TASK ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS.
It usually consists of forces affecting a business directly and for which a business person can manipulate to suit the objectives of the organization. The variables includes;
- Customers-all enterprises rely on external customers for survival.the customers may be an individual/an institution/government/another firm. The manager must understand customer needs inorder to satisfy them.
- Suppliers-this are institutions/people who supply materials to the organization.they must provide quality inputs at competitive prices and offer fast delivery
- Employees/H.R-they are also the internal customers of the business who should be satisfied first.they supply labour to the organization and on their part,employees work to meet their own personal,social and economic needs.the management must ensure a harmonious working relationship so that employees are satisfied and the organization achieves its objectives.
- Trade unions- this is a group of employees come together to fight for their rights within an organisation.the management must maintain good relationship with unions for effective running of their organization.some organisations allow their employees to belong to some unions while others put stringent rules and regulations to bar them from joining this unions.
- Owners/shareholders-this are technically the owners of the organization through stock ownership.those with majority shares have the ability to influence the running of the organization.the management must ensure that the shareholders intrests are protected in terms of cutting down of costs and maximizing profits.they usually exercise their powers through voting in general meetings.
- Financial institutions/Resouces-they supply the much needed capital to run the business and include commercial banks,investment banks,insurance firms etc which advance loans,provide investment opportunities and insure business against risks.the management must ensure a good working relationship with them.
- Company policies and objectives-this are rules and regulations necessary to govern business operations.the management can change the policies and objectives to suit what it wants to achieve at a particular time.
- Business structure-this refers to the formal arrangememt of functions and relationships of people and work and is divided towards achievement of the set objectives.
- Physical resources-these are the tangible facilities which belong to the business e.g. buildings,furniture etc.
- Personal aspects-this includes things like labour relations,recruitment practices appraisal system etc.
- EXTERNAL/MACRO/CONTROLLABLE ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS.
This is the environment prevailing outside the organization for which a business can not manipulate but has to try and fit within the prevailing factors.it takes the advantage of opportunities and tries to avoid the threats.
- Social-cultural factors-relates to changes in the society in terms of beliefs,values,norms ,customs,traditions,religion,literacy,lifestyle differences,changes in consumption pattern, a business person must take care of this factors in order to succeed in business within a particular locality. The advancement in technology has seen so many changes in consumer preferences. Kenyans are no longer buying cassette tapes with the advent of CDs, DVDs, and USBss. (Madura 2007)
- Demographic factors-this are the characteristics of the population in terms of; age, total population,geographical dispersion,dependency ratio,birth rate,level of education,gender,marital status,religion,occupation,social class,incomea business person must target each group of consumers with the products they like. Ie a growing population creates a wider market for goods and services,better education and jobs for consumers who has improved taste and preference and demanding for high quality goods and services.
- Legal factors-this relates to changes in the laws and regulations that govern business operations.businesses must be careful to keep laws and anticipate ways in which change in this laws will affect their businesses e.g. tobacco law,media bill,mututo law etc.
- Political factors-this relates to ways in which changes in government and government policies can influence business.in a county with political instability,businesses are threatened.business may also influence government actions through lobby groups and in some countries,the business community fund their preferred candidate/party to form the next government ie capitalist/free,command /central/command and mixed economy.
- Economic factors-this relates to changes in the wider economy and influences the consumers willingness and ability to buy goods and services.a counrys economy will go through decline,recession ,recovery and boom.a business has also to consider the purchasing power of consumers inorder to offer affordable products to them and also the nature of demand for their products. Other economic variables to consider include;intrest rates,level of inflation,consumers income,borrowing rates,tax rates,business cycles at particular times.this economic factors will help a business to decide when to invest and when not to invest in a business.
- Technological factors-technology is the level of know how,available for doing specific things.managers need to be aware of changes in technology taking place in environment so as to update themselves and their organization.technology changes provide opportunities for business to adopt new breakthroughs,innovations,inventions to cut costs and to develop new products.
- Competitors-this are businesses that offer similar products to what the organization is offering.businesses that do not compete effectively are often confronted with a likelihood of being eliminated from business.customers are usually the beneficiaries of stiff competition in the industry e.g. Kenyan telephone users are benefiting greatly from competition between safaricom,airtel,orange and yu.The competitors issues can be clearly viewed using a model developed by Michael porters five forces model
- Rivalry among firm-this is where firms come together and rival so as to attain the highest market share.
- Bargaining power of consumers-this is a case where there are many consumers who have different bargaining powers and thus consumers will buy goods in the places they wish to.
- Bargaining power of suppliers-this is a case where there are numerous buyers and few suppliers.therefore dictating the price to charge e.g. the case of oil.
- Threat of substitues-this is where one can either opt one substitute instead of the other e.g. coffee/tea.when one adopts one substitute good,the other good is faced with a threat.
- Threats of new entrants-when one experiences great profits,other firms may come in so as to enjoy the same profits causing one to be faced with a serious challenge.
CLASSIFICATION OF COMPETITORS.
- Leaders-they are usually innovative in nature and are regulary first to bring new products in market place e.g. safaricom.they usually use the following policies;harassment,innovation,fortification(competing ie safaricom and airtel in terms of calling prices and is usually in futility) and confrontation through price wars.
- Follower-tend to copy what the leaders do. ie they usually copy ,imitate and capitalize on the leaders weaknesses.
- Challenger-tries to overtake the market leaders.
- Niche-marketers-this is a marketer or an organization which offers some kind of specialized product/service referred as unique service provider(U.S.P) e.g. equity bank that usually targets the low income groups.
KEY ISSUES ABOUT A COMPETITOR THAT A MARKETER SHOULD BE AWARE OF.
- Nature of competition and the products available in the market.
- The organization position in the market
- Objectives of the competitors.
- Size and power of the competitors.
- Resources of the competitors
- Procedures and practices of the competitors.
TYPES OF COMPETITIONS IN THE INDUSTRY.
- Generic competition-this is a type of competition where products are used for the same purpose through the products that are in different industries e.g. cinemas and football matches compete as forms of entertainment.
- Enterprise competition-this are firms that produce similar products e.g. bata shoe company and tata company competing as forms of foot wear.
- Brand competitions
- Monopolies
- Monopolistic
- Oligopolies
- Perfect competition.
- Publics-this is any group that has an actual or potential interest in a firm and assists a firm to achieve its objectives.the following are the types of publics;
- Media publics.
- General public
- Environmental groups
- Consumer organisations
- Local public e.g. neighbours and community
- Financial publics
- Government bodies
- Trade unions
- Local community.
9)Physical environment-this includes factors such as climate and infrastructure e.g. roads, water supply,electricity,telephone etc.
TOPIC FIVE
PRODUCT
Product refers to anything that can be offered to a market for attention, use, or consumption that might satisfy a want or need. It includes,
- Services
- Ideas e.g. consultancy firm on lectures where people purchase your idea and pay e.g. Elijah kupata invention of security alarm.
- places e.g. visits to museum;a need is satisfied when one pays
- physical objects
PRODUCT CLASSIFICATIONS.
- Durability and perishability.
Durable goods normally service many uses and are consumed or used for a very long period of time. Perishables are used once or a very short period of time. Other products which are taken into account in this stage includes tangible items which are usually felt,touched or seen while intangible products can’t be felt, touched or seen e.g. services.
- Consumer and industrial goods.
- Consumer goods-this are products bought by consumers for their own final consumption.they can be classified in four main categories.
- Convenience goods-this are goods that consumers know enough about them before purchasing them.they buy the goods on a day to day basis. they purchase them with minimum effort thus no evaluations are made and frequently e.g. newspapers,foodstuff,airtime,milk,bread,tea leaves etc.
- Shopping goods-this are goods that consumers may want to compare in terms of features,quality,price,suitability and style in several shops before making a purchase.most of them are desirable e.g. furniture,clothes,tv set etc.
- Speciality goods-this are goods that consumers have a strong brand preferences for and they are willing to spend a lot of time and effort in locating them because they are not in any shop ie they are got from specific outlets.most are very expensive and have a unique brand identification and owning them carries a status in it e.g. tv,cothing.
- Unsought goods-they are products consumers may not yet be aware of and if they are aware they may not place so much meaning to them and have to be convinced of their importance inorder to purchase them e.g. insurance policies.a customer do not ordinarily purchase the product unless convinced through personal selling and are not in the budget.
- Industrial goods-they are products bought by businesses for further processing or for use in conducting their operations.they include.
- Material and parts-this includes raw materials such as wheat which is to be processed into flour then to bread and parts such as wires,yarn(for sweaters).the finised forms must be attached to others to function well e.g. for electricity lines,copper(finished product) is needed as well as some sufurias.
- Capital equipment-includes machinery equipment and installations such as generators,computers,wardrobe etc.
- Supplies and business services-this includes services such as banking,warehousing,insurance and cleaning services and also includes repair and maintenance services to machines as well as supplies of stationery.
- Component parts-this are finished products themselves but which need to be attached for another good for them to be useful e.g. tyres which are got from rubber(finished product).
- Standardized and custom made goods-standardised goods are produced in large quantities for use by everyone while custom made goods are produced based on customer specifications.
PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE STAGES.
INTRODUCTION.
Like people,products go through a life cycle in that they are born,grow,age and eventually die or are replaced. Product life cycle refers to sales history of a product beginning with development ending with sales decline.
- Development.
This is the pre launch phase where a company undertakes research and development as the product progresses from experimentation to the tangible product.confidentiality is maintained by keeping information away from competitors.
- Introduction.
- Customers are innovators.
- Sales are low
- Profits are low.
- Demand is low because many people do not know the product.
- Degree of competition is low.
- Promotion is always informative advertising to create awareness.
- Intensive distribution is used to increase market share and exclusive distribution can also be used to maintain the brand image.
- A company can use two new product pricing strategies.
- Market skimming pricing-firms sets high prices to skim off profits as quickly as possible before competitors enter the market.it is ideal when one is targeting the innovators,early adopters,high income earners and customers with high social status.
- Penetration pricing-a company sets low prices so that I can build a market share quickly and attract more customers before competitors enter the market.its ideal when one relies on economie of large scale,creation of barriers to entry to shy away competitors from venturing in this market,to increase the market share of the company and when the products demand is elastic.
- Growth stage.
- Customers are early adopters.
- Demand starts rising.
- Sales and profits also starts rising as many customers become aware of the product
- The degree of competition increases as more competitors come in due to growth in sales.
- Promotion shifts from informative to persuasive.
- Sales promotion activities are also undertaken.
- Prices may remain high for sometime but may start to fall as competitors come in.
- Selective distribution is used.
Growth stage strategies.
- Increasing the frequency of use.
- Increasing the number of users.
- Finding new uses of products.
- Changing packaging sizes,labels or product quality.
- Maturity stage.
- Customers are the early majority and late majority.
- Demand,sales and profits continue to increase for a while until they reach a peak after which they start to level off.
- The degree of competitition intensifies and promotion will include both persuasive and comparative advertising techniques.
- Prices start to reduce as discounts are given inorder to maintain the sales.
- Intensive distribution is used.
- Decline stage.
- Customers are the laggards
- Demand,sales and profits are low because of the new products that have come in or technological changes that make a product obsolete.
- Prices are low as huge discounts are given,degree of competition is low as many of them leave for other new products.
- Intensive distribution is used.
- A company may undertake the following strategies to extend the life cycle of the product.
- Making cosmetic changes to the product e.g. changing shape,colour or packaging.
- Changing the formula by adding some ingredients(perfumes) or removing others.
- Changing the price. Ie huge discounts,psychological pricing etc.
- Changing the retail outlets through which the product is distributed.
- Introducing new advertising campgains e.g. cocacola.
Strengths of PLC
- Enables the company to forecast future behaviour of the product and prepare to handle such behaviour
- Enables the company to decide on the marketing strategies to use at each stage of the PLC
- Assists the company to decide when to launch a new product and when to discard an existing product
- Enables the company to decide on the number of products it can maintain at each stage of the PLc
- Guides on the promotional methodology that can be used in different product stages.
- Assists in targeting the right type of customers.
- Helps marketers to understand the different stages that a product goes through.
Weaknesses of PLC
- It over-emphasizes the importance of developing new products which is a rather expensive method and cannot be pursued by smaller less financially-stable companies
- It is not empirical as some products have an endless life
- The four stages of the PLC are not distinct i.e. there is no clear distinction between them – a product may be at the introduction stage yet it may have characteristic of the maturity stage.
- PLC concepts can be interfered with by marketing managers.ie finding new customers for the product in new geographical territories.
- High cost of research and development
- Variation in customer types in different stages thus targeting is a problem
- It is not able to maintain confidentiality especially at development stage.
NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS.
New products has three forms.
- New to the world-this is a truly unique product that is there is no other product like that in the market.
- Improvement /revision to the existing products.this are products that are significantly different from existing goods in that they provide improved performance.
- Imitative products-they are new to a particular company but not new to the world.eg sqny and not sony or addidias instead of addidas.
A company would develop a new product for the following reasons.
- To improve the quality of its products
- To meet the pressure of competition. Ie defend market share position e.g. KBL developed new products when it realized it was facing competition from castle.
- To utilize excess capacity if the company has excess machines,capital,manpower,raw material etc.
- To sustain the company growth once a product has reached the maturity stage.
- To respond to environmental force-produce products that are environmental friendly.
- To respond to new technology.
- To establish a position in a new market e.g. equity bank –equitel.
STEPS IN NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT.
- IDEA GENERATION–
This is the creation of ideas .the ideas can be generated from;
- Customers ie
- Customer ways-this is where you ask customers their need and wants which are not being met.
- Focused group discussions-this is where you get a group of customers and introduce a topic to them.the fact will be towards their needs and lifestyle.
- Suggestion boxes or complaint letters from customers.
- Mails sent
- Telephone calls
- Projected lists.
- Company laboratories-when marketers are conducting experiments they may get an idea ie they may make discoveries by chance coming up with good ideas about a product.
- Competitors-ask competitors what they like about competitors products.also buy the products yourself,analyse it and then make a better product.
- Sales representatives and middlemen-because there is constant touch with customers,they can provide first hand information about customers needs and their complaints.
- Marketing research firms-they are consultants who find out and tell you what is wrong with your product and possibilities of new ideas in the market.
- IDEA SCREENING
Sloot and drop poor ideas as early as possible.it tries to reduce the number of ideas to one attractive practical few.in improving ideas and screening items the company should avoid;
- Drop errors-occurs when a company drops a good idea.
- Go errors-occurs when a company permits a poor idea to move to other development stages.it is very important for one to screen the ideas because the product development costs rise substantially with each successive stage.
GUIDELINES TO BE USED WHEN SCREENING IDEAS.
- The existing or potential demand for the products-are there sufficient number of people in the market and do they have purchasing power?.
- The marketing compatibility-this is the extent to which the proposed product matches with the existing marketing variables.
- The environment and social standard compatibility-this is the extent the proposed new product harmonizes with the environment and social standards.
- Durability-this is the expected life cycle of the product.
- The long term expected sales growth-this is the extent to which the new product will generate profits for the company.
- Technical capability-this is the degree to which the proposed product matches with the existing production facilities e.g. time management to handle the product
- BUSINESS ANALYSIS-
A company should evaluate the business attractiveness of the proposal and it is looked at from the point of view of sales,costs involved and the profits you expect to make.it makes use of forecasting techniques which include use of historical data of similar products or through customer always in order to find out buyer intentions.
- PROTOTYPE PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT-
This is where a company answers the question whether the product idea can be translated to a technically and commercially feasible product.it is the stage of making the idea concrete(reality).the research and development develops a prototype(model) that satisfies the following criteria.
- consumers see it as having the desired attributes.
- It perfoms safely under normal use and conditions.the model can be produced with the budgeted manufacturing costs.
- Must pass the funs size,shape,taste and scope.
- The company must choose a brand name in this stage and should be in the package.
5)MARKET TESTING-
This involves testing the product to learn how customers and ideas react to its use,handling and purchasing the actual product.First,one selects a representative sample of consumers using probability and non probability techniques. The specific towns and markets are then visited. The length/duration of the test is the next step where the period that one carries the trial test is determined. How the product functions and how many people are buying or trying frequency of purchase and overall attitude towards the product is essential. Finally decide on the action to be taken based on the tested results.
6)COMMERCIALIZATION
This is the final stage in which a company makes a final decision to launch the new product in market. A company can decide to launch a product by;
- Roll out introduction-this involves starting with a few towns when introducing to its entire country with time.
- Crash introduction-here,one introduces the product into the national level market at once ie the product is available country wide. A company has also to decide the time of the launch e.g. text book can be launched at the beginning of the year. The launching can be single,locational,international,national or regional. Market testing gives the management enough information to make a final decision about whether to launch a new product.When commercializing a new product, the following factors have to be taken into account:
- When (timing)
- Where (Geographical strategy)
- To whom (target market prospects)
- How (introductory market strategy)
REASONS WHY A NEWPRODUCT FAILS.
- Inappropriate promotion being used.
- Stiff competition from the competitors.
- Highly priced commodities.
- Poor quality products.
- When the new product has not penetrated in the market fully.
- When the new product fails to meet the customers specifications.
- When the frequency of use is minimal e.g. stamps
- When the product have already reached decline stage.
FIVE LEVELS OF A PRODUCT
- Core benefit – The fundamental service or benefit that the customer is really buying.
- Basic products – Is the physical/ tangible product
- Expected product – Set of attributes and conditions that buyers normally expect and agree to when they purchase a product.
- Augmented product – This is what customers desire beyond their expectations e.g. warranty,repair services,toll free help no etc.
- Potential product – This encompasses all the augmentations and transformations that the products might ultimately undergo in the future.
PRODUCT MIX DECISIONS
PRODUCT MIX VS PRODUCT LINE:
1.Product Mix of a company refers to a set of all products, lines and items that a particular seller offers for purchase to buyers / consumers. Conversely,
2.A company’s product line refers to a group of products closely related (due to the fact that they function in a similar manner) and are sold to the same customer groups, marketed through the same type of outlets or fall within a given price range. They satisfy the characteristics below: –
Satisfy similar needs.
Consumed together
Produced together
Distributed similarly or
Fall within the same price range
- Product Mix Depth refers to the number of variances offered for each product in the line (for example, in the soft drink industry Crest comes in three sizes and two formulations ‘regular’ and ‘mint’ – thus Crest has a depth of six.) This can be used to expand a company’s product portfolio if it is made deeper by adding more product variances to each product e.g. adding more sizes in the packaging variation or adding more formulations.
- Product Mix Length: Refers to the total number of items in its product mix. For example in the soft drink industry, a company like Coca Cola International may include Coke, Sprite, Fanta and Crest. Thus, if we want the average length of a Coca Cola soft drink product then we may calculate it as follows:A company can use product mix length to expand its product portfolio by introducing more brands of its items to the existing ones and making sure its current product lines are full ones.
- Product Mix Width: Refers to how many different product lines the company carries (for example Coca Cola International has one product line: soft drinks).
- Product Mix Width can be used to expand a company’s product portfolio if the company introduces new product lines like beer, water, juice or bread for example.
- Consistency-how closely related the individual product lines are in end use,production requirements,distribution channels or in some other way.
3.Product mix assortment
Is the set of all products and the items that a particular seller offers for sale to the buyers.
4.Product item
Is a distinct unit within a brand or product line that is distinguishable by size, price,appearance or some other attributes.
INDIVIDUAL PRODUCT DECISIONS.
This is a name,term,sign,symbol or design or a combination of the terms intended to identify the goods and services of one seller or group of sellers and to differentiate them from those of competitors.basically,it is a companys asset.
The brand identifies the seller/maker.it can be a name,trademark,logo or symbol.the sales of this branded product are granted exclusive rights on how the product will be used and thus the degree of competition is very low thus few firms remain in market ie one or two firms selling the branded product.counterfeiters are therefore knocked out.
It usually adds to the product ia a bottle of soda with the name coca cola is perceived to be of high quality than one in un-marked bottle which is said to be of low value.it also helps consumers in identifying products that might benefit them.branding also says something on the product quality and consistency ie same features,benefits and quality each time they buy.
It usually gives sellers several advantages(one spends less on marketing).it also offers legal protection for unique product features that otherwise might be copied by competitors.ie Toyota can offer majors such as lexus;Toyota and Scion brands each with numerous sub-brands e.g. Camry;Prius;Matrix;Yaris;Tundra and landcruiser.
VALUE/IMPORTANCE OF BRANDING FOR CUSTOMER AND MARKETERS.
- Brands facilitate purchasing-brands are often easily recognized by consumers and because they signify a certain quality level and contain familiar attributes,and also assits consumers make quick decisions e.g. Honda in terms of level of quality,engineering,relative status and generally the cost.without branding,how could we easily tell the difference between a Honda and Toyota without looking very closely?.
- Brands establish loyalty-overtime and with continued use,consumers learn to trust certain brands.
- Brands protects products from general competition and price competition-strong brands are somewhat protected from this as the brands are more established in market and have a more loyal customer base,neither competitive pressure on price nor retail-level competition is as threatening to the firm.
- Brands reduce marketing costs-firms with well-known brands can spend relatively less on marketing costs than firms with little known brands because the brand sells itself.people have become familiar with some logos of companies so advertisements don’t need to explain who the company or what it does .people just know.
- Brands are assets.brands are also assets that can be legally protected through trade marks and copy rights and thus constitute a unique ownership for the firm.this is to ensure that the value of their brands is not diluted with counterfeit merchandise or sales through unauthorized dealers.
- Brands impact market value-having well known brands can have a direct impact on companys bottom line.
- PACKAGING
This involves designing and producing the container/wrapper for a product.it has shifted from attracting attention to describing the product,to making the sale.companies are realizing the power of good packaging to create immediate consumer recognition of a brand.today,a competitive world,the package may be the sellers best and last chance to influence the buyers.poorly designed packages can cause headaches for consumers and lost sales for the company.sometimes even seemingly small packaging improvements can make a big difference.
In recent years,product safety has also become a major packaging concern.we have all learned to deal with hard-to open “child-proof packaging”.the company also must heed to growing environmental concerns ie go “green” by reducing their packaging and using environmentally responsible packaging materials.
This usually ranges from simple tags attached to products to complex graphics that are part of the package.it helps or identifies product /brand.helps in describing the product ie who made it and where it was made;its contents;how it is to be used and how to use it safely.it promotes the brand,support its positioning and connect with customers.
E.g. pepsi;recrafted graphics on its soft drink to give the brand a more meaning and social relevance to its youth audience.
FUNCTIONS OF PACKAGING AND LABELLING
- Physical protection against damage,spoilage and pilferage-this is because products typically pass through several stages of handling between manufacturing and custonmer purchases and a package must protect its contents from damage.
- Assists in marketing the product as packaging nowadays have been use as a promotional tool.
- Cost effectiveness-although packaging must perform a number of functions for the producer,marketers and consmers must do it at a reasonable cost.sometimes changes in packaging can make packages both cheaper and better for the environment.a good example is given of compact disk manufacturers who once packaged music cds in two containers,a disc-sized plastic box inside a long cardboard that fit into the record bins in stores. Consumers protested against waste of long boxes and the recording industry and finally agreed to eliminate the cardboard outer packaging altogether.
- Portion control-single serving or single dosage packaging has a precise amount of contents to control usage e.g.
- Salt is in suitable size for individual households.
- Aids control of inventory ie selling sealed one litre bottle of milk rather than having people bring their own bottles to fill themselves.
5.Convinience-packages can have features that add convenience in distribution,handling,stacking,display,sale,opening,reclosing,use,dispensing,reuse,recycling and ease of disposal.
6.Security-this is the important role played by packaging in reducing security risks of shipment;packages can be made with important tamper resistance to deter tampering and can also have tamper evident features to indicate tamper.
7.Information transmission-packages and labels communicate how to use,transport,recycle or dispose off the package or product.with pharmaceuticals,food,medical and chemical products,some type of information are required by government.some packages and labels are used for track and trace purposes.
8.Containment or agglomeration-small objects are typically grouped together in one package for reasons of efficiency e.g. a single box of 1000 pencils requires less physical handling than 1000 single pencils.liquids,powders and granular materials need containment.
9.Barrier protection- this is mainly from oxygen,water vapour,dust.some packages contain dessicants/oxygen absorbers to extend shelf life.
- PRODUCT ATTRIBUTES
This usually ranges from;
- Quality
- Performance level.
- Consistency ie freedom from defects and deliver the targeted level of performance.
- Development-TQM model is used.
- Features should be
- The style ie appearance should have no effect on performance.
THE CONSUMER ADOPTION PROCESS
Marketers must understand this process in order to build an effective strategy for early market penetration.
THE CONSUMER ADOPTION PROCESS
– This process describes how potential customers:Learn about new products,try them and Adopt or reject them. Adoption is an individual’s decision to become a regular user of a product. The consumer adoption process is later followed by the consumer-loyalty.
Stages In The Adoption Process:
The consumer adoption process focuses on the mental process through which an individual passes from first hearing about an innovation to final adoption.
Adopters of new products have been observed to move through the following five stages: –
- Awareness – The consumer becomes aware of the new product but lacks information about it
- Interest – The consumer is stimulated to seek information about the product
- Evaluation – The consumer considers the costs and benefits of using the product
- Trial – this is usually based on the evaluation to buy to estimate the value of using the product.
- Adoption-if the trial is favourable,adopt the new product and use it regulary.
Adopter Categories.
1)Innovators-this are the first 2.5% of the buyers who adopt new products. They comprise of the young,better educated and consumers who have higher incomes. They are more willing to take risks.
2)Early adopters-these are the next 13.5% of buyers and are guided by respect and are the opinion leaders in the communities. They adopt new ideas early but carefully e.g. preachers,musicians etc.
3)Early majority-these are the deliberate consumers.they are the leaders but are careful in what they purchase.they represent 34% of the buyers.
4)Late majority-these are the skeptical or suspicious buyers.they adopt an innovation only after the early majority has tried it.they represent 34% of buyers.
5)Laggards-these are the traditionalist or conservative people.they are suspicious of changes and adopt an innovation only when it has become something of a tradition itself. They represent 16 % of the buyers
TOPIC SIX
PRICE /PRICING.
This is the amount of money charged for a good or service.This is the sum of value consumers exchange for the benefit of having or using a good or service. This is the market value of a product as it is offered in market.
FACTORS AFFECTING PRICING DECISIONS/FACTORS TO CONSIDER WHEN PRICING.
- Marketing objectives-a marketer must consider the marketing mix in terms of product design,distribution and promotion inorder to form a consistent and effective marketing programs
- Cost-consider the cost of production,cost of distribution and marketing expenses.
- Profit maximization-the management must consider profits expected before setting the final price.
- Organizational considerations-prices must always be set by management rather than by the marketing department/sales
- Market and demand for the product-a markter must understand the relationship between price and demand for the product(factors affecting demand).
- Environmental elements-prices must take into consideration the existing competitors prices.
- Prices of substitute goods.
- Intermediaries demands
- Suppliers-if an organization suppliers notice that prices of an organization products are rising,they may seek a rise in price of their supplies(inputs) to that organization
10.Inflationary conditions prevailing in the country
11.income effects of the consumers.
IMPORTANCE OF RICING.
- Price is a means of regulating the economic activities ie keeping the economy in balance.
- Price has a considerable impact on consumer perception ie a marketer can either increase the price and emphasize on quality or lower the price and emphasize on bargaining.
- Price is one of the four pcs that can be changed quickly to respond to changes in the environment.
- Price determines the entire marketing strategies of a company
PRICING OBJECTIVES.
This gives the directions to the whole pricing process.determining what your objectives are is he first step in pricing.when deciding on pricing objectives,you must consider.
- Overall financial,marketing and strategic objectives of the company.
- Objective of your product/brand.
- Consumer price elasticity and price points.
- Resources you have available.
SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES.
- Maximize long-run profit
- Maximize short run profit.
- Increase sales volume(quantity).
- Increase monetary sales.
- Increase market share.
- Obtain a target of return on sales.
- Stabilize market price.
- Ensure company growth.
- Maintain price leadership.
- To desensitize customers to price.
- Discourage new entrants into industry.
- Match competitor’s prices.
- Encourage exit of marginal firms from the industry.
- Survival in the market.
- Avoid government investigation/intervention.
- Obtain/maintain loyalty and enthusiasim of distributors and other sales personnel.
- To be perceived as fair by customers and potential customers.
- Social,ethical or ideological objectives.
STEPS INVOLVED IN PRICING PROCESS.
A firm must set a price for the first time when the firm develops or acquires a new product,when it introduces its regular product into a new distribution channel/geographical area and when it enters its bid on new contract work.
low Quality high
| Economy | Penetration | |
| Skimming | Premium |
price
high
price strategies matrix.
Kotler describes a six step procedure for price setting.
- Select the price objective-ie maximum current profits,maximum current revenues and current sales growth.
- Determine the demand-analyse the demand curve ie demand curve is normally inversely related to price.
- Estimate the cost-demand sets a ceiling on price that the company can charge for its products and the company sets the floor ie fixed/variable.
- Analyze competitors costs,prices and offers-benchmark your costs against competitors cost.
- Select a pricing method ie markup,target return,value,sealed bid etc.
- Select the final price-pricing methods narrows the price range from which the company must select its final price.in selecting the final price,the company must consider additional factors including psychological pricing,influence of other marketing mix elements on price,company policies and objectives,pricing policies and objectives and legal constraints.
METHODS OF PRICING/DETERMINING PRICE LEVELS.
1.Cost-based pricing.
- Mark-up pricing-this involves adding a standard markup to the product cost .markups are higher on seasonal items,slower moving items and items with high sewerage and handling costs.a high mark up however may be disadvantageous if competitors prices are low.ie hotels peak mostly in holidays.
Advantages of high mark up.
- It is advantagious in that sellers can determine their costs more easily and hence by basing their prices on cost,they simplify the pricing task.
- Where all firms use this pricing method,prices tend to be similar hence price competition is minimized.
- Most people feel that pricing method is fair to both buyers and sellers.
- Target return pricing-the firms determines a price that will yield its target rate of return on investments.if the firm doesn’t reach expected unit sales,the marketer can prepare a break even chart to learn what would happen at other sales levels based on different prices.the manufacturer will then use different prices and estimate the probable impact on sales volume and profits.
2.Value based pricing.
- Perceived value pricing-companies based their price on customer perceived value.they see the buyers perception of value and not the sellers cost as the key to pricing e.g. a car manufacturer may price his car at a million while his competitor charges 90,000.he may explain the difference due to longer warranty of the car,superior services,superior durability etc.the customer will be convinced that such a car operating costs will be lower and hence buy the more expensive car.
- Value pricing-companies charge a low price for low quality goods and a high price for high quality goods.the price must reflect a high value offer to customers.
3.Competition based pricing.
v.Going rate pricing-the firms basis its price largerly on competitors prices.smaller firms follow the leader changing their prices only when the market leaders change theirs rather than when their own demand or costs change.some firms may charge a slight premium or a slight discount but they preserve the amount of difference to minimum.
Vi sealed bid pricing-this is where a company submits sealed bid for jobs.the firm bases its price on expectations of how commpetitors will price and for a firm to win a contract,it has to submit the lowest price bid,however it can not price below costs and neither can it compromise on quality,hence a firm will bid a price that will maximize the expected profits in the long –run.
Pricing strategies
This are defined as long plans and they are not limited,compared to ways of establishing prices.
1.Premium Pricing
Use a high price where there is uniqueness about the product or service. This approach is used where a substantial competitive advantage exists. Such high prices are charge for luxuries such as Conrad Cruises, Savoy Hotel rooms,airplnes etc
2.Penetration Pricing
The price charged for products and services is set artificially low in order to gain market share. Once this is achieved, the price is increased. This approach was used by France Telecom and Sky TV.
3.Economy Pricing
This is a no frills low price. The cost of marketing and manufacture are kept at a minimum. Supermarkets often have economy brands for soups, spaghetti, etc.
4.Price Skimming
Charge a high price because you have a substantial competitive advantage. However, the advantage is not sustainable. The high price tends to attract new competitors into the market, and the price inevitably falls due to increased supply. Manufacturers of digital watches used a skimming approach in the 1970s. Once other manufacturers were tempted into the market and the watches were produced at a lower unit cost, other marketing strategies and pricing approaches are implemented.
Premium pricing, penetration pricing, economy pricing, and price skimming are the four main pricing policies/strategies. They form the bases for the exercise. However there are other important approaches to pricing.
5.Psychological Pricing
This approach is used when the marketer wants the consumer to respond on an emotional, rather than rational basis. For example ‘price point perspective’ 99 cents not one dollar
6.Product Line Pricing
Where there is a range of product or services the pricing reflect the benefits of parts of the range. For example car washes. Basic wash could be $2, wash and wax $4, and the whole package $6.
7.Optional Product Pricing
Companies will attempt to increase the amount customer spend once they start to buy. Optional ‘extras’ increase the overall price of the product or service. For example airlines will charge for optional extras such as guaranteeing a window seat or reserving a row of seats next to each other.
8.Captive Product Pricing Where products have complements, companies will charge a premium price where the consumer is captured. For example a razor manufacturer will charge a low price and recoup its margin (and more) from the sale of the only design of blades which fit the razor.
9.Product Bundle Pricing
Here sellers combine several products in the same package. This also serves to move old stock. Videos and CDs are often sold using the bundle approach.
10.Promotional Pricing
Pricing to promote a product is a very common application. There are many examples of promotional pricing including approaches such as BOGOF (Buy One Get One Free).
11.Geographical Pricing
Geographical pricing is evident where there are variations in price in different parts of the world. For example rarity value, or where shipping costs increase price.
12.Value Pricing
This approach is used where external factors such as recession or increased competition force companies to provide ‘value’ products and services to retain sales e.g. value meals at McDonalds.
REACTIONS TO PRICE CHANGES.
Price cut may have many meanings ie,
- product about to be replaced by newer models
- fault in the product
- the sellers are abandoning the segment ,so they want to do away with the stock as fast as possible.
- reduction in quality.
Price increase on the other hand may have many meanings ie
- the product is so hot ie has become unobtainable, so better buy it soon,
- Improved value etc.
TOPIC SEVEN
PLACE/DISTRIBUTION/TRANSPORTATION.
CHANNELS OF DISTRIBUTION.
A channel of distribution is the route or path followed by a product as it moves from the producer to the consumer/final user.
TYPES OF DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS USED.
They are mainly classified into two main categories ie
- Direct/zero channel.
- Indirect channel.
- DIRECT MARKETING/ZERO CHANNEL(PRODUCER-CONSUMER).
This is the distribution system where no intermediary is used and the company sells the product directly to the consumer.
REASONS FOR GROWTH OF DIRECT/ZERO MARKETING.
- High cost of driving,traffic congestion and packing headaches. Have made people prefer goods to be directly delivered to their homes.
- Lack of enough/inadequate/insufficient time.
- The market is now comprised of high market nitches(narrowly defined groups),each with different preferences.
- Long queues at counters.
- Electronic communication is growing and products can now be sold through the internet.
ADVANTAGES OF DIRECT MARKETING.
- Home shopping is convenient.
- Saves time
- Customers can do comparative shopping by browsing the internet.
- Customers benefit by learning about available products without meeting a sales person.
- It can be timed to reach customers at the right moment e.g. at home.
MAJOR CHANNELS FOR DIRECT MARKETING.
- Direct mail.
- Tele marketing-calling through telephone.
- Kiosk marketing-this is placing machines in busy places such as airports and bus stops where customers can get specific goods e.g. stamps,sweets and soft drinks a good example is the automatic vending machines.
- Internet.
2.INDIRECT CHANNELS.
- One level channel e.g. producer-retailer-consumer.
- Two level channel e.g. producer-wholesaler-retailer-consumer.
Producer-agent/broker-retailer-consumer.
- Three level channel e.g. producer-agent/broker-wholesaler-retailer-consumer.
Producer-wholesaler- jobber-retailer-consumer.
CHANNEL CONFLICT.
This are disagreements among marketing channel members on goals and roles ie who should do what for what rewards.eg
- Horizontal conflict-refers to same level (among retailers).
- Vertical conflict-this are conflicts between different levels e.g.(wholesalers and retailers).
CAUSES OF CHANNEL CONFLICT
- i) Role incongruities-A role is a set of prescriptions defining what the behavior of the position member should be.
- ii) Resource scarcities-Disagreement over the allocation of some valuable resources needed to achieve a given goal may cause conflict
iii) Perceptual differences-Perception refers to the way an individual selects and interprets environmental stimuli in relation to objective reality.
- iv) Exceptional differences-Channel members have expectations about the behavior of other channel members. These expectations are predications concerning the future behaviors of other channel members. These predictions could turn out to be inaccurate but non-the less channel members take action based on these predictions.
- v) Decision Domain disagreements-Channel members’ explicitly or implicitly carve out for themselves an area of decision making that they feel is exclusively theirs. In contractual channel system, such as a franchise, these decisions domains are quite explicit and are usually spelled out meticulously in the franchise contract. But in more traditional, loosely aligned channels made up independent firms; the decision domains are sometimes “up for grabs”. Hence conflict can arise over which member has the right to make what decisions.
- vi) Goal incompatibilities-Each member of the marketing channel has his/her own goals and if these are incompatible, conflict arises.
vii) Communication difficulties-Communication is the vehicle for all interactions among the channel members, where such interactions are cooperative or conflicting. Breakdown in communication can lead to conflict in the channel.
MANAGING CHANNEL CONFLICT
In practice, conflict is usually spotted after it is well developed and obvious. This is because the potentially negative effects of the conflict may have a head start and may be already out of hand.
It is therefore better for the channel manager to have some kind of early warning system using perception surveys, marketing channel audit and distributors advisory councils or channel members’ committees.
- Dual compensation-this is applied when conflict exist between direct and indirect channels. The goal is to move the indirect channel from the position of potential adversary for direct sales force to one of partner for direct sales force.
- Activity based compensation/discount-it is used to manage cross-channels conflict or conflict between channels of differing cost structures and capabilities.it is applied by paying a channel a specific discount if it performs a measurable task or function.
- Compensation for market share-it is usually applied to direct versus indirect conflict, direct sales representatives is compensated based on total market in a territory.it motivates the direct representatives to partner with indirect channels to maximize territory volume.
- Economic solutions-compensate channels fairly for function performed and help direct channels away from functions that create destructive conflict.
- Control-put a structure around a channel strategy to limit the potential for undue destructive conflict.
RESOLVING CONFLICT.
Rosenberg suggested methods that a channel manager may use to resolve conflict. These are:-
- a) A channel wide committee- comprising of manufactures, distributors and retailers representatives
- b) Joint goal setting by the committee.
- c) A distribution executive position may be created for each major firm in the channel. The individual in this position will be responsible for exploring the firms distribution related problems, create awareness of the possible effects of conflict.
- d) Arbitration, which is advantageous as it is fast, is less expensive than litigation, preserves secrecy, involves the industry experts and most importantly confronts the problem in the early stage when it is easier to solve.
FACTORS TO BE CONSIDERED WHEN SELECTING A DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL.
- Customer characteristics-this include type of customer,geographic dispersion of buyers ie location to manufacturers,customer buying habits and the outlets they purchase from.
- Product characteristics-this includes perishability,product usage(industrial-direct or household-indirect).
- Company characteristics-this includes a company objectives,financial status ,past channel experiences and the desired degree of channel control.
- Middle men characteristics-this includes financial status,storage capacity,availability and the services they offer.
- Competitive characteristics-for some products,it is preferable to use the channels that are used by other competitors e.g. fast moving consumer goods.
- Environmental characteristics-this includes economic,political,legal,social,cultural and technologica factors that may affect the channel selection.
- Nature of the goods ie heavy,bulky etc
- The number of terminals
- Transportation cost
- The distance to be covered ie water and air are mainly used for long distance products.
- Speed and urgency of the goods.
- The packaging requirements
- Availability of the channel
- Flexibility of the channel to be used ie can it be used in the interior regions?.
RETAILING.
This refers to all activities involved in selling goods or services directly to final consumers for their personal, non-business use.
Retailer-Business whose sales come primarily from retailing
DESCRIBE WAYS IN WHICH ADAVNCES IN TECHNOLOGY HAVE ENHANCED THE LEVEL OF CUSTOMERS SERVICE PROVISION BY RETAILERS/GROWING IMPORTANCE OF RETAIL TECHNOLOGY.
- Check-out scanning systems.
- Online transaction processing.
- Electronic fund transfer.
- Electronic data interchange.
- In-store television
- Improved merchandise-handling systems
- Rfid
- Wireless transactions.
ROLES OF RETAILERS.
This roles are mainly classified into three main scopes;consumers,wholesalers and manufactures. They include.
- Bringing easy access to goods.
- Offers a wide variety of goods.
- Stocks goods for consumers
- Bulk breaking large stocks for conumers as well as wholesalers and manufacturers.
- Offers aftersale services.
- Ensures regular supply of goods
- Offers credit facilities.
- Offers outlet for goods.
- Offers storage facilities
- Offers financial services by buying from the wholesalers and manufacturer.
- They usually necessitate or conduct product promotion for goods.
- Offers financial advice to product response by consumers.
WHOLE SAILING
Wholesaler refer to a firm engaged primarily in wholesailing activity,while wholesailing refers to all the activities involved in selling goods and services to those buying for resale/business use.
FUNCTIONS OF WHOLESAILING.
– Selling and promoting
– Buying and assortment( a group of similar things having different sizes,colour and quality) building
– Bulk-breaking
– Warehousing(storage).
-Price stability –This is possible mainly due to storage that happens .During low production seasons,stored goods are released in the market and stabilize supply in the market.
– Transportation
– Financing
– Risk bearing
– Market information(advice)due to contact with manufacturers
– Management services and advice
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN WHOLESALERS AND RETAILERS.
WHOLE SALERS RETAILERS.
-Sells goods from his warehouse -Sells goods from shop.
-Can be located else where -Located at complicated centers to offer
what is supplied.
-need large capital base to start -need smaller capital to start.
-need large storage space -need smaller storage space.
-buys in bulk and stocks in large quantity-buys at smaller quantity and sells in
smaller units.
-sells on cash basis -sells in credit and cash.
-specialise in buying and selling few -buy and sell different commodities
types of commodities
FUNCTIONS OF MIDDLEMEN/INTERMEDIARIES.
- Contacting function-this involves being link between the producer and the consumer.
- Market feed back(communication)-they relay information to consumers about the product and collect feedback from the customers to the manufactures.
- Breaking the bulk-this is in smaller quantities that customers can afford.
- Physical distribution-this is transportation of prducts from producer to the consumer.
- Demand stimulation function-through advertising,personal selling and sales promotion.
- Advancing credit to their clients
- Storage function-warehousing goods on behalf of the producers.
ROLE OF IT/E- COMMERCE IN DISTRIBUTION.
E-commerce /It has improved distribution system and enhanced communication among members.it involves use of computers,mobile phones,internet,electronic payments e.g. Mpesa etc.
- 1.Use of mobile phones and emails helps channel members to communicate in fast manner on issues regarding distribution of products.
- 2.Helps in monitoring and branding movement of goods.
- 3.Use of EDI among channel members helps them to always to be in touch to each other.
- 4.Marketing may also be carried out by channel members through internet.
- 5.Use of computerized system in storage helps channel members to store their goods in modern way which is more effective.
- 6.Use of electronic payments among channel members helps to pick transaction and is also cheap compared to traditional methods e.g. ATMS,MPESA etc.
- 7.Use of modern ways of ordering goods e.g. making online orders and use of emails assists in saving costs and continuity in production processes.
- 8.Use of e-sourcing in locating suppliers.
INTENSITIES OF DISTRIBUTION.
Intensities of distribution involve determining the number of intermediaries that will be used at each level and includes:
- I) Intensive Distribution
This is the strategy whereby a product is distributed by as many outlets as possible. This is used for products, which the consumer requires a great deal of location convenience e.g cigarettes, Newspapers milk, bread, Scratch cards,soft drinks etc.
- II) Selective distribution
Manufacturers select only a few distributors for a new product and is especially. For speciality and shopping goods e.g. Appliance like fridge, cookers.
Advantage of selective Distribution
- a) It enables the produce to gain adequate market coverage
- b) Easy to control the channel
- c) Less costly compared to intensive distribution strategy.
III) Exclusive distributionThis is getting into an agreement with a particular middle man where the manufacturer gives exclusive rights to the marketer to distribute the product.This severely limits the numbers of intermediate or channel members. Used when the producer wants to maintain the control of the service levels. Also here, the middleman in return agrees not to carry any merchandise of the competition e.g. Bata, Simba Telecom (Safaricom Dealer),Marshall,-exclusive distributor of electronics and DT Dobie for Mercedes.
Advantages of exclusive distribution
- The rational behind this strategy is that the specialization in one line may greatly increase sales and profits particularly the premium price obtained through exclusive distribution
- Certain service level is maintained.
- Control by the manufacturer
- Standardized price
Disadvantages
- a) Requires greater partnership between the seller and re –sellers e.g. Bamburi.
- b) Training of channel members thus costly.
LOGISTIC MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS.
This are activities that support the physical distribution of goods and they include;
- Warehousing-this is performance of administrative and physical functions associated with storage of goods and materials.the functions include receiving-identification-inspection-storage of goods for issue to production process-retrieving goods.
- Transportation-this is the movement of finished goods from production operation to consumer using various modes of transportation e.g. road,air ,water and rail.
- Order processing-this is the efficient receipt of orders,processing the orders,ensuringefficient delivering and preparation of invoices for payment.
- Stock/inventory control-this is maintaining of stocks in sufficient levels to avoid overstocking and running out of stocks before the next delivering.
- Clearing and forwarding-clearing and forwarding agents are service providers who assist importer/exporter to arrange for transport,documentation and customs clearance for international shipment.
TOPIC EIGHT
PROMOTION/INTEGRATED MARKETING/COMMUNICATION MIX.
Promotion is a function of marketing mix and is a technique used in creating awareness on the companys product as well as the company itself.
ELEMENTS OF PROMOTION.
1.ADVERTISING.
This is any paid form of non-personal presentation of ideas(goods or services) by an identified sponsor.
QUALITIES OF ADVERTISING/ACTIVITIES INVOLVED IN DEVELOPMENT OF AN ADVERTISING PLAN.
1.Public presentation-advertising is public in nature because many people receive the same message and sellers know that motives for purchasing products will be publicly understood by the target population.
2.Pervasiveness-this permits the seller to repeat the message to many times.it allows the buyer to receive and compare the messages of various competitors.it also indicates the sellers size,power and success.
3.Amplified expressiveness/dramatise-this provides the opportunities for dramatizing company and its products through artful use of print,sond and colour.
4.Impersonality-the audience does not feel obliged to pay attention or respond to the advertisement .it is usually a monologue infront of the audience ie a one way communication.
IMPORTANCE /VALUE OF ADVERTISING/PROMOTION.
- Used to inform consumers about a new product or an existing product by mentioning the features of the product.
- Used to persuade consumers to purchase a particular brand where such a brand is believed to be offering quality for the value of money spent by the consumer.
- Used in comparing one brand directly or indirectly to another or to existing competitors brands available in the market.
- Used to remind consumers that they need to purchase the product.
- Indicate new uses of an existing product.
- Give information of price changes, special offers etc.
- Build brand recognition.
- Increase market share and demand.
- Increase the number of retail outlets.
- Build overall company image.
- Reach new segment/areas.
- Develop overseas markets
MEDIA USED IN ADVERTISING.
Advantages
- It is usually very attractive and entertaining,hence difficult to ignore.
- It appeals to both the literate and illiterate and is viewed by all irrespective of age,gender etc.
- The combination of visual and audio effects and dramatization makes it very effective.
- Advertisements can be aired at the most appropriate time when the targeted audience is most likely to be reached.
Disadvantages
- Television sets are generally expensive and out of reach for many Kenyans.
- It is a costly medium to use.
- It may be affected adversely by mechanical break downs,power failures and unfavourable weather conditions which make reception poor.
- Viewing is limited to areas with electricity or people who can afford batteries.
- The advertisements may not appeal to all the viewers due to age,gender or cultural bias.
- Coverage is not so large compared to other means .
- Newspaper,magazines and trade journals.
Advantages
- Newspapers have a wide circulation,appropriate for businesses operating nation wide.
- They are relatively cheap for the reading public.
- Some newspapers are published in local languages.
- Many magazines aim at reaching specific population groups.this suits the needs of advertisers who wish to reach these groups.
- Messages in newspapers and magazines have an aspect of permanence which radio and television advertisement do not have
- Some magazines are quite informative and entertaining,hence attracting a wide readership
Disadvantages.
- Newspapers which have a national circulation are not effectivein targeting specific
- Illiterate consumers may not be reached.
- Newspapers have a short life span for each edition e.g. it is very unlikely for people to read past newspapers
- Some magazines are quite expensive,hence have a limited readership.
- Readers may ignore the advertisements altogether due to familiarity or they may just be interested in specific information due to lack of time.
Advantages.
- They are attractive.they therefore catch the attention of prospective customers easily.
- They have a fairly long span.
- Their reach is wide.so many people get to see them.
- Some are modified to rotate in order to accommodate more than one advertisement.
- Many people can view them at one time.
Disadvantages.
- Some may require security to avoid vandalism.
- They are expensive to design, put up and maintain.
- Interferes with the environment (space) by being unsightly and causing unnecessary obstruction of general view.
- They may be ignored by busy motorists.
- Posters
Advantages.
- The pictures are appealing to the illiterate
- They reach many people as they can easily be distributed.
- They are cheap to produce.
- A mixture of colour can be used to target a certain geographical region ie can be localized.
- They can stay for a long period of time if they are not interfered with.
Disadvantages.
- Permission may be required to put them up.most of areas have posters warnings.
- They have a very short life as they hardly last for more than a few days due to some harsh weather conditions.
- They make the areas in which they are put up untidy.
- They are easily ignored by busy people as they are silent.
- They do not appeal to illiterate people
- They are brief
Advantages.
- Many people own radios hence radio advertisement have a very wide reach.
- Radios are used by a large number of people meaning the reach of the advertisement will be multiplied.
- Radio advertisements can be made entertaining thus hold the attention of the intended audience.
- The advertisements can be broadcast in many local languages to increase the resch even further.
- If a catchy,familiar tune is used with the advertisement,the listeners tend to internalize it.
Disadvantages.
- Poor timing may lead to the advertisements being missed by the desired target group.
- It is expensive especially so when they are aired at prime time and if they are lengthy.
- It could be a source of irritation to the listeners of popular programmes especially if aired in the middle of the programmes or if they take too long.this irritation may distract the audience from advertisement.
- Radio transmission may be interrupted by poor weather or mechanical breakdowns,making the advertisement less effective.
- The advent of many radio stations makes advertising expensive as one may have place advertisements in all of them if the product being advertised is meant for the general public.
- Exhbitions
- Videos
- Slide
- Transport(vehicles).
- Ad post-notice boards along major streets
- Ad shells-shelter places with roofing;waiting bays for vehicles.
- Bronchures-small booklets containing pictures and information about a product or a service.
- Cinema-used to transmit visual and sound messages about products before the start of a show,at the interval ,and at the end of the show.it is done at cinema theatres and at mobile cinema shows which are common in rural areas.
- Neon signs
FACTORS/CRITERIA TO CONSIDER IN SELECTING THE MOST APPROPRIATE MEDIA FOR ADVERTISING.
- Cost element-refers to amount of money to be spent in advertising.select the most cost effective media.
- Frequency-this is the number of times the public will hear a single advert.the higher the frequency the better the impression created.
- Impact-this is the effect of an advert on the target audience and it is measured through the ability of audience to remember the advert.
- Target group-various market segment use different media and the choice of media must be related to the audience targeted.eg royco cubes would be advertised via radio as opposed to newspaper.
- Acceptability-this relates to the media house and whether they will accept to advertise a particular product e.g. Christian median stations may not accept to advertise alcoholic beverages,cigarettes and illegal substances.
- Readership-this is the coverage of media in terms of number of people who will have a direct access to a particular publication incase of print media and those who are literate to understand the message.eg current newspaper circulation stands at 300,000.
- Physical characteristics-the mediums characteristics ie visual aspects,colour movement etc have to be considered in relation to the type of advertisement run.tvs,newspaper and magazines show this attributes.
- Quality of production-where the quality of advertisement is of great consequence,then the medium that produces quality advertisements is preferred.
- Nature of the product-a product meant for general consumption will be advertised in a medium that has very wide reach.eg hospital machines and meedicines would be advertised through trade journal to which doctors subscribe.
FACTORS TO CONSIDER BEFORE COMING UP WITH AN ADVERTISING BUDGET.
An organization needs to budget in order to ensure that its expenditure does not exceed its planned income.
- Competitors activities –we should have parity.
- The market size/share
- Available funds
- The nature of the product the company is selling ie consumer or industrial goods.
- Prevailing government policies.
- Frequency of the advert-this is important because adverts are charged differently according to the timings of the day/nigh times.
2.SALES PROMOTION.
This comprises of short term incentives designed to increase the purchasing behavior of consumer through a variety of rewards and are meant to increase sales.
IMPORTANCE /VALUE OF SALES PROMOTION.
- To increase sales.
- To introduce a new product.
- To encourage sellers to re-stock the items or increase their stocks e.g. free refrigerators to stock soda/water.,brand shelf given to supermarkets free to stock a given product.
- Encourage the consumers sales force to put in greater effort ie giving of bonuses and certificates.
- To clear existing stock-this avoids carrying costs as well as sitting on money
- To promote unsought products.
- To remain competitive in the market
TECHNIQUES USED IN SALES PROMOTION.
- Consumer promotions-this are designed to increase short term sales by inducing final consumers to try a new product or to increase purchase of an existing product. The effort of company is directed towards the end user of the product. This technique is also known as the pull strategy.ie producer-wholesaler-retailer-consumer.;but the arrow starts from consumer backwards.The media /techniques used usually includes;
- Free samples.
- Cash discounts.
- After sale services.
- Free gifts.
- Free demonstrations.
- Price deals ie decreasing.
- Sweep stakes- this is a method of gambling in which each person pays a small amount of money and is given the name of a competitor before a race/contest and the person who has the name of the winner receives all the money.
- Rebates-cash refund to buyer for purchasing a product
- Coupons(pieces of paper carrying a certain value).
- Trade promotions-This includes getting wholesalers and retailer to carry new items or increase their stocks by giving them certain incentives. This encourages them to advertise the product and give it more self-space. The effort of organization is directed towards the traders or intermediaries.it is also called the push This is exhibited by producer-wholesalers-retailers-consumers. The arrow is a forward one. The media/techniques used includes;
- trade discounts
- allowances
- commissions
- competitions
- free demonstrations
- credit facilities
- free training-technical products/machines
- technical support e.g. installations
- rebates-cash refund given to resellers on providing proof on sales.
- push money-manufactures pay retail people to promote products for them.
- trade shows
- trade contents
- point of purchase display for attention and dealer loaders- This is a premium given to a reseller to encourage development of special diplay/produced offering.
- Sales force promotions-this are incentives given to the sales force to support current or new products or getting the sales people to sign up new contracts with manufacturers and suppliers.the media used to target sales force promotions include;competitors,financial or non financial incentives ie cash rewards,free training,bonuses and commissions.
- Personal selling-this involves face to face interaction with one or more prospective purchasers for the purpose of making presentations,answering questions and procuring orders.
ASPECTS OF PERSONAL SELLING.
- Professionalism-this involves training sales people to the selling process.the steps to effective selling include;
- Prospecting and qualifying-the company will find the leads by examining data sources such as newspaper and directories,organizing trade shows,using telephone and mails.qualifying involves contacting the leads to access their level of interest and financial capacity.
- Pre-approach/establishing needs-the sales person needs to learn as much as possible about the prospect company ie their needs,purchasing power,who is involved in purchase decision etc.
- Approach-the sales person should know how to greet the buyer,to get the relationship off to a good start.
- Presentation and demonstration-the sales person tells the product story using the AIDA formula that is getting attention,holding intrest,getting them to desire and obtaining attention ie Attention,Intrested,Desire and Action.
- Overcoming objections-this involves dealing with any resistance towards the product or the company.it could be as a result of preference for established supply sources,reluctance to give up something,pre-determined ideas and pleasant experiences with sales persons.this should be overcomed by;Maintaining a positive approach,Clarifying objections andTurning objections into a reason for buying.
- Closing –the sales person needs to know the right psychological moment to close the sale e.g. physical actions e.g. nodding in agreement,positive comments or asking questions.
CLOSING TECHNIQUES.
- Asking for an order.
- Indicating what buyer will lose if they don’t order now.
- Asking the buyer whether they want A orB or helping them make choices on colour or size.
g.Follow-up and maintenance-This is necessary to ensure customer satisfaction and repeat business(customer comes many times).it includes scheduling a follow up call to ensure proper installation,instructions are followed and servicing of the product.
2.NEGOTIATION.
Negotiating skills are important in order to reach an agreement on price and other terms of sale.a sales person should win the order without hurting the profits of the company.
3.RELATIONSHIP MARKETING.
This involves building a long-term supplier customer relationship inorder to ensure repeat business.it is based on the promise that ,important customers need focused and continuous attention e.g. calling them,visiting them,taking them to dinner or lunch,making useful suggestions about their business etc.eg equity bank offers calendars,pens success cards etc.
4.PUBLIC RELATIONS/PUBLICITY.
This involves a variety of programs designed to promote a companys image or its individual product.a public is any group or individual who has an actual or potential intrest in a companys ability to achieve its objectives.eg customers,employees,shareholders, suppliers,government and financiers.
FUNCTIONS OF PUBLIC RELATIONS.
- Press relations-this involves news and information about the organization in the most positive way.
- Product publicity-this include sponsoring effort in order to publish specific product.
- Corporate communication-this is promoting understanding of the organization through internal and external communication.
- Lobbying-this involves dealing with legislators and government officials to promote certain issues within a company or defeat certain laws and regulations.
- Counseling-this involves advising management about public issues and about the companys position and image.it includes advising them on action to take in the event of a product failing to meet customer expectations.
TOOLS OF PUBLIC RELATIONS.
- Publications-this is published material used to reach and influence the target market e.g. annual reports,articles , company newsletters,audio visual materials etc.
- Events-this are special events such as conferences,seminars,outings,anniversaries,sports ,cultural sponsorships that are used to reach the target market.
- Speeches-talks before large audiences especially at trade association meetings inorder to build the companys image.
- Public service activities(corporate social responsibility)-this is contributing time and money to good courses in order to build a good public image/public good will e.g. giving funds to children homes,building roads,financial support in education sector e.g. wings to fly programme etc.
- News-this involves developing a good story concept and getting the media to accept to feature it.
- Identity media-because companies compete for attention a company needs a visual identity that the public immediately recognizes e.g. logos on uniforms,stationery,business cards etc.
5.DIRECT MARKETING.
This are direct communications with carefully targeted individual consumers to obtain an immediate response and cultivate lasting customer relationships.the new direct marketing models include:advances in direct marketing include emergence of catalog companies,direct mailers and telemarketers.
BENEFITS AND GROWTH OF DIRECT MARKETING.
BENEFITS TO BUYERS;
- Easier to know the current models in the market as per ones needs
- Convenient
- Wealth of comparative information is allowed.
- Interaction and immediate feedback is possible
- Privacy is enhanced.
- Enhances greater product access and selection.
BENEFITS TO SELLERS;
- It is a tool for customer relationship buildings ,better targeting and customerization.
- It can be timed to reach prospects at just right moment.
- Higher readership and response is enhanced.
- There are numerous internet and online benefits which one enjoys ranging from,
- Reduce costs and increased speed and efficiency.
- Avoids expenses of rent,insurance utilities(owning a store).
- Improve efficiency of channel and logistic functions.
- Costs less than communicating on paper through the mail
- Greater flexibility is enhanced in terms of production quotas and the needs of customers.
- It is usually a global medium-ie across all nations.
CUSTOMER DATABASE AND DIRECT MARKETING
Customer database-this is an organized collection of comprehensive data about individual customers or prospects including geographic,demographic,psychographic and behavioural data.
Database marketing-this is the process of building and maintaining customers data for the purpose of contacting and transacting with the customers.it is commonly used in B2B and service retailing(hotels,banks and airlines). It makes use of a customers mailing list – a set of names,addresses,telephone numbers etc and customer database-contains much more information e.g. past purchases,personal information,family information etc.
The database kept by the firm assists in,
- Identifying the prospects.
- Deciding which customer should receive a particular offer.
- Deepening customer loyalty(ie information,gifts etc).
- Reactivating customer purchases(knowledge of past purchase is kept,gifts,certificates and promotion.
FORMS OF DIRECT MARKETING.
- Face to face selling.
- Tele marketing-using phones to sell directly to customers.
- Direct mail-letters,ads,samples,fold outs are used.the media used here include;voice mail,email,fax mail and physical mail.
- Catalog marketing-this is mainly through print,video or electronic catalogs.
- Direct response television marketing-this is direct marketing via television,including direct response television advertising or commercial home shopping channels.
- Kiosk marketing- refers to information and ordering machines placed in stores and airports.it is different from vending machines because a kiosk does not dispense the actual product.
- Internet/online marketing-this is marketing conducted through interactive online computer systems which link consumers with sellers electronically ie internet and commercial online services.
TOPIC 9
CUSTOMER CARE.
This refers to activity of looking after customers and helping them with complaints and problems. It involves provision of service before and after purchase. Customer care is also a third party provider that takes customers calls,answers their questions,address their concerns,and solves their problems etc, and submits detailed reports on such activities to the principal(client).
It involves putting systems in place to maximize your customer’s satisfaction with your business.
THREE AREAS/ELEMENTS IN CUSTOMER CARE.
- Expand your definition of services-how you define services shapes every interaction you have with your customers services should provide customers with satisfaction in essence the customers should walk away pleased at the result of transaction and not just content but actually happy.a happy customer will continue to be a buying customer and a returning customer.
- Who are your customers-customers,buyers and clients want to pay a fair price for quality service or product and feel satisfied they have paid for services or product and receive what they have paid for in return.it is important to listen to customers and do research,their habit and what they want and expect.
- Developing a customer friendly approach-by customer friendly,we mean viewing customer as most important part of your job.
SOURCES OF FREE CUSTOMER INFORMATION.
- Business contacts
- Local business reference libraries.
- Your local authority;business link/chamber of commerce.
- Internet.
- Uk trade for information on export markets.
- Forex ie N.S.E.
CUSTOMER SERVICE QUALITIES
Customer service=accountability delivery.
Professionals who constantly deal with customers inside or outside the company need to strive for certain qualities to help them answer customer needs.the professional qualities to be emphasized always relates to customer wants.
BASIC PROFESSIONAL CUSTOMER SERVICE QUALITIES.
- Friendliness-associated with courtesy and
- Empathy-appreciate customers wants and circumstances.
- Fairness-customers want to feel and receive adequate attention and reasonable answer
GREETING THE CUSTOMER.
The purpose is to create and maintain a welcoming environment and we can achieve this by;
- Looking good-be well groomed.
- Smiling
- Eye contact directly to the customers eyes
- Shaking hands-professional hand shake is expected.
- Being attentive-slightly lean towards the customer and nod always to indicate you are listening.
ASPECTS OF CUSTOMER SERVICE.
- Attitude and appearance-a customer service representative must be congenial,presentable and approachable e.g. when communicating on phone they should be pleasant and an understandable voice be used. The concern of the customer is the top priority and the representative can not allow his/her mood or other internal issues destruct his/her from this priority.
- Convenience ie easy to approach.
- Follow up-this can be done by sending an email or by calling or even visiting the customer.
- Communication-e.g. if you are doing repairs on someonescar,calling the customer and updating him on progress or sending an email to keep him upraised of the situation cold be a very smart way to proceed.
SOURCES OF CUSTOMER COMPLAINS.
- Defect cost by production or service failure and employee mistakes.
- Marketing over promises
- Misleading marketing
- Customer errors and unreasonable expenses.
- Customer is incorrect but makes a reasonable mistake.
- Dissatisfaction on use of product and its effects.
- Poor customer services-rudeness.
- Discrimination in serving customers
- Customer exploitation in terms of prices, quality and quantity.
- Long time spent in responding to their urgent problems.
- Media-mainly social media.
- Phone calls by customers
- Mails sent by customers
- Internal employees.
- Analyzing the order history patterns
- Direct feedbacks.
WAYS TO REDUCE CUSTOMER BASED PROBLEMS.
- Effective labeling/giving clearing directions
- Pro-active education-this is a cost effective way to resolve common customer problem e.g. Vodafone pro actively calls customers three weeks after cell phone activation.
- Easily accessible customer assistance.
HANDLING CUSTOMER COMPLAINS.
There will always be customers who complain after completing the sale. Like customer objections,don’t view complains negatively.rather they are often a very good way to;
- Obtain valuable customer feedback on products.
- Assess customer attitudes to company policies.
- Address customer needs that were not previously identified.
It is evident that customer complaints can be a good selling opportunity.
METHODS/PROCEDURE FOR HANDLING CUSTOMER COMPLAINS.
| Respond to all complains promptly. Ask the customer to state clearly in detail, step by step what happened. | When you are satisfied, you shall have all the facts, restate the situation to the customer to make sure there is no misunderstanding. |
| Let them get it off their chest first. This does much to diffuse a great deal of customer’s anger/resentment. | At this point, it is often clear what the customer has done wrong or where the fault lies. |
| Be a good listener | Make a decision quickly and don’t leave the customer waiting for a solution. |
| Interject only occasionally using good questioning techniques to clarify a point or keep things moving in a logical fashion.Dont offer an opinion at this point. | If it is the store fault or a defective product, then rectify it immediately. If it is the customers fault, make sure they understand clearly what happened and how to fix it. |
| When you fell that they have given a full statement of their problem, you may ask a few questions suggested by their comments. | It is often good public relation to compromise or help them out of their problem. It often does not cost much and the spin off word of mouth advertising is more than worth it. This is one way to build customer loyalty and repeat business. |
ROLE PLAYED BY CUSTOMER CARE.
- To create customer loyalty-after offering good customer care for them in terms of advertising, their problems and complains in proper manner; customer loyalty is created.
- Addressing customer’s complaints.
- Solving problems of customers.
- To enhance sales performances in that good customer care is likely to attract a large customer base hence improving sale performance.
- It is used as a marketing tool.
- Creates a good corporate image of the firm.
- To receive customers.
- To handle customers complaints
- Handle difficult customers.
TOPIC 10
SERVICE MARKETING.
Service refers to any act/performance that one party offers to another that is essentially intangible and does not result in the ownership of anything.
SPECIAL CHARACTERISTICS OF SERVICES.
- Intangibility-services can not be seen,tasted,felt,heard or smelt.
- Inseparability-services are produced and consumed simultaneously.
- Heterogeneity(heterogeneous)-services are variable since they depend on the provider.
- Perishability-services can not be stored e.g. medical care.
- Ownership-services do not result in ownership of anything.
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD SERVICE QUALITY.
- Should have support services ie it should augment the actual product.
- Should be well labelled.
- Should be well packaged.
- Should have a brand that identifies it with the maker.
SERVICE CONCEPT.
This is based on the idea that actual service offering can be broken down into a number of levels relating to customer need satisfaction,benefits and features. Three levels can be identified.
- Core benefit service-This relates specifically to the customers needs. The core benefit satisfies the need or solves the problem.
- Expected service-this relates to customers’ expectations of what kinds of services are available to satisfy their need. The expected service reflects standards required or expected by customers to satisfy their needs.eg in a bank one expects that polite language is used,professional knowledge is applied by the staff etc.
- Augmented service-this means making the service better in some way and it is the means by which service providers differentiate their offering in an attempt to influence customer choice. Extra features over and above the expected service can be added to make the service more attractive to prospective customers. Innovation is the key to make a service stand out from the competition.eg in the banking sector,we have the corporate section where we have corporate customers who are usually served differently according to class.
ELEMENTS OF THE SERVICE MIX.
- Service-this involves superior quality,a well known and trusted brand image,unique features and extended guarantees.
- Price-involves added value,special discounts and preferential credit terms(free for a new customer brought).
- Promotion-this involves innovative advertising campgains,loyalty promotions(points) added,special offer,public relations e.g. sponsorship e.g K.CB in terms of safari rally,safaricom,equity etc.
- Place-This involves extensive availability(in many parts g. equity bank),innovative methods e.g. telephone banking,agents and careful selection of quality channels(mpesa).
- People-This involves highly trained staff, better customer care,greater efficiency,personal attention and specialized skills.
- Process-This involves advanced technology e.g. for counting money,efficiency systems e.g. introduction of ATMs to avoid queing in banks and fast response
- Physical evidence-This involves comfortable surrounding,superior décor(decoration) e.g. for wedding organisers they gather in hotels,schools,banks.Qualifications and evidence of professional standing(e.g. certificates being placed on walls) and a strong recognizable corporate image(similar uniform) and supporting documentation.
WAYS OF DEVELOPING BRAND STRATEGIES FOR SERVICES.
- Line extension(existing brand,existing service category)-this is using a successful brand name to introduce additional items in a given service category under the same brand name such as new flavours,forms,colours,added ingredients as well as different packaging sizes in respect to a product.
- Brand extension(existing brand,new service category)-using a successful brand name to launch a new service in a new category.
- Multibrands-(new brand,existing product category) ie offering new band in same category.
- New brands-(new brand,new service category) may be appropriate if none of the existing brands is appropriate for a new service entering new market.
- Mega brand strategies-this focuses on marketing dollars only in brand that can achieve number one or number two market share in their categories.
PRODUCT SUPPORT SERVICES MANAGEMENT.
- Training the current employees/hiring new ones.
- Increasing the quantity of service by giving up some quality.
- Industrialise the service by adding equipment and standardized production.
- Harnessing technology ie data mining,cloud computing etc.
TOPIC 11
EMERGING TRENDS AND ISSUES IN MARKETING.
- Use of advanced technolog1y-computers;ict advancement
- Emergence of customer care services department to handle financial matters only.
- Tele marketing.
- Globalization-this is a process whereby different systems and parts of a related trade,function as a closely-knit system at the international level. Communication and transport have vastly improved and affects many aspects of marketing from competition policy to monetary policy and agricultural policy.
- Mergers and joint ventures of institutions so as to increase the institutions capital base.
- HIV aids and drug abuse menace.
- Pollution
- Corruption .
- Tight budget and allocating,spending and measuring of ROI is a running battle in marketing departments.
- Social media grow up.
- Games-marketers already have been adding games to their sites and doing product placement deals with sites and doing product placement deals with sites and using games to more customers along the decision making path.they are shaping their websites with questions,tasks and rewards designed to keep customers engaged with all kinds of brands,from insurance to cars.
- Bar codes-recent adoption including snap tags including brand logo with most of smart phones now capable of scanning the codes,and advertisers are using them to link in store shoppers to manufacturers website or connect to a nearest store.
- Tv talks-interactive tv advertising by use of satellite and cable companies fitted with set-top boxes.
- Digital wallet-electronic payment and couponing systems with electronic payment systems coming up e.g. mpesa,airtel money and equitel.
- Intrapreneurialism grows-being highly agile and flexible.
- Metrics mature-this is the ability to measure every click ,tweet and page view and is both a blessing and a curse and is used to gage a companys performance.
- Emergence of consumerism movements-this is an organized movement of citizens and government agencies to improve the rights and power of buyers in relation to sellers
- Emergence of environmentalism movement-this is an organized movement of concerned citizens and government agencies to protect and improve peoples current and future living environment.
- Cloud computing.
- Adoption of new marketing strategies e.g. e-marketing to search for more customers.
- Competitors coming up with new improved product.
- New government polices i.e. media bill.
- Emergence of fraudsters producing counter fake products.
- Changing customer basis and needs.
- Emergence of new product life cycle stages ie fads ,fashions and style products.
CHALLENGES POSED BY THIS TRENDS.
- Some trends and issues require more resources in order to meet the new trends and issues e.g. more funding.
- Government policy which might really affect the new trend/issue.
- New/more competitors coming into market.
- Changing market needs and wants.
- Coverage of wide market area-due to globalization aspect.
- Changing the approach to get more customers or maintain the existing ones.
WAYS OF COPING UP WITH CHALLENGES.
- Adopting new marketing strategies.
- Employing more resources in marketing teams.
- Coming up with legal measure to deal with fraudsters.
- Reaching a wide market to stay relevant.
- Coming up with model or design that would move customers.