2.1 Procedures of Starting a Business
- Identification of a business idea
- Development of a business plan
- Location of a business demand evaluation
- Registration of the business
Choice of the business organization
Business name - Trading licences / permit
- Start-up and management of the business.
- All entrepreneurs are business people – though not all business people are entrepreneurs.
- Entrepreneurs tend to be more innovative than ordinary business people and end up developing a business plans.
2.1.1 Means of Generating a Business Idea
- identifying a need
- brainstorming
- building on ones skill, hobbies or interests
- spotting a market niche
- listening to what people say
- attribute listening
- gaining from waste
- look to see and listen to hear
- research
- importing an idea
- day dreaming
- Spin off from employment.
2.1.2 Identifying a Need
A need can be an opportunity and indeed a consumer buys to satisfy need. Abraham Maslow in his humanistic hierarchy of needs, physical needs to very high personalized needs. Therefore identifying an unidentified or unserved need is a sure way of generating business ideas.
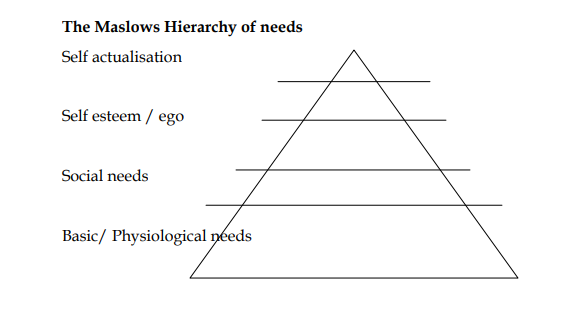
1. Basic or physiological needs
The first and the most basic need such as thirst hunger and sleep – in the process of satisfying these needs, entrepreneurs can generate a lot of business ideas- such as cloth stores, food stores, building materials etc.
2. Safety and security needs
Human beings require these and entrepreneurs can generate ideas in the process of satisfying them e.g security, watchmen e.t.c.
3. Social needs
Generally speaking to need should be accepted in the society e.g membership clubs, beauty clinics et..c
4. Self esteem or ego
the need only needs recognition e.g need for luxury cars cellular phones e.t.c
5.self – actualization
The need to prove the ability in one’s self i.e self fulfillment – research institutions opportunity to do something in one’s ability.
2.1.3 Brain Storming
This is a process of detaching analysis of an idea from the actual ideas. The idea may or may not be related to a given product. In brainstorming even silly and stupid ideas may be generated.
2.1.4 Building on One’s Skill, Hobbies or Interests
business ideas can be generated through
- personal interests and hobbies
- Copying or improving somebody’s ideas. ( skills)
2.1.5 Sporting a Market Niche
Entrepreneurs usually look for gaps in the growing markets, identifying market sections which are not being utilized.
2.1.6 Listening to what People say.
These are people who simply say or speak their needs e.g if these good bus services
2.1.7 Attribute listening
This method of generating business ideas is based on changing the way one looks at something in order to fins a new use for it. It attempts to answer the question – what do we do with this product.
2.1.8 Gaining from Waste
What would appear waste can be used- say recycles to create a new opportunity.
2.1.9 Others
By soliciting ideas by interview, reading, observations, listening
2.2. The Process of Screening a Business Idea.
After generating business ideas- it is important that some evaluation through a screening process be made. The screening process is a systematic evaluation ideas in order to select the best idea which would suit one. The screening process must be done carefully, objectively, soberly and without any emotions. The business idea screening is required even when there is only one idea to consider. This is because this is a stage of starting a business that may be not be profitable or may be difficult to run.
The screening process must therefore evaluate the following
1. Personal Evaluation
- the objective for going to business
- personal interests
- The degree of commitment to the business or others e.g family.
- Personal Skills
2. The self SWOT analysis – this aims at analyzing ones
- Strengths
- Weaknesses
- Opportunities
- Treats
This will help achieve the desired goals- the
S- Relates to the internal capacity of self or organization
W- Are subjective
O- Relates to the external environment to self or organization
T- Are objective.
2.2.1 The Importance of this Screening Stage include;
- In order to develop a strategic profile.
- To provide a framework to assess the current and future plans
- To act as a control technique when conducted periodically
- To get realization ( reality) on the activities
The SWOT components
Strengths – these are positive internal conditions such as - Distinctive competence
- Adequate finances.
2.2.2 Components of the SWOT Analysis (importance of self evaluation)
The screening process or evaluation helps identify;
1. Strength
- Distinctive competence
- Adequate finances
- Access to economies of scale
- Good innovation ability
- Proven management
2. Weakness
- Lack of key skill
- Internal operations problems
- Low morale
- Poor track records
- Weak internal image
3. Opportunities
- Potential customers
- Potential goodwill
- Health
- A favourable social
4. Threats
- strong competitions
- Adverse government policies
- Political instability
- A designed economy mismanaged economy
- Unfavorable legislation
Market evaluations
The aim is to create assurance of adequate market
The main components include
- Consumer demand analysis
- Product price and placements
- No. of competitors in markets.
An analysis of availability of raw materials in terms of
- Adequacy
- Reliability
- Price
Analysis of providing technology in terms of
- Appropriateness
- Affordability
An analysis of skills available
Analysis of the government policies.
2.2.3 Characteristics of a Good Business idea.
- Easy to manage and involve minimal risk.
- Does not require excessive capital investments
- Offers a good returns on capital
- The idea has scope for growth, expansion and diversification
- Comparative with owner’s goal and interest
- Not against expectation of the society
- Has a short gestation period
- Has a readily available market
- Easy to exit when necessary.
2.3 The Generation and Sources of Business ideas
Generalization of business ideas
- Entrepreneurs have the ability to see opportunities in whatever environment they happen to be
- They are sensitive to people’s needs
- They use people’s problems as opportunities of a business
- The entrepreneurs can use several methods to help generate and test new ideas.
2.3.1 Methods of Generating ideas or Business Opportunities
Focus groups – i.e where a moderator leads a group of peoples though an open , in –depth discussion through which new ideas are shared. Apart from generating new ideas, the focus group is an excellent method of screening ideas.
Brainstorming
The brainstorming method allows people to be stimulating to greater creativity by meeting with others and participating in organized group experience. When using brain storming the following rules must be obeyed.
- No criticism nor negative comments
- The wilder the idea the better ( freewheeling)
- Quality of ideas is desired
- Combinations and improvements of ideas are encouraged.
Problem inventory analysis
This method used individuals in a manner that it forcus groups to generate new ideas e.g consumers given a list of problems in a general product category and discuss the various problems in each product category normally used to test new products.
Creative problem solving – is a method of obtaining new ideas by focusing on the parameters such as
- Brainstorming – group method of obtaining spontaneous ideas
- Reserve brainstorming – a group method of obtaining new ideas but by focusing on the negative i.e by finding fault.
- Brain writing – is a form of brainstorming which gives participants more time to think than brainstorming which dwells on spontaneous ideas the participants write their ideas on a special form.
- The Gordon method- is the method of developing new ideas when the individual are unaware of the problem.
- It ensures that the solution is not clouded by pre-conceived ideas or behavioral pattern
- Checklist method.- is a method of developing new ideas through a list of related issues
- Free association method
A new idea is developed through a chain of world association. Forced relationship it is a technique that asks questions about an object or idea in an effort to develop a new idea it follows the following five steps
- Isolate the element of the problem
- Find the relationships between these elements
- Record the relationship in an orderly way
- Analyze the resulting relationships to find ideas pattern
- Develop new ideas from the pattern.
Collective notebook method
Develops new ideas by a group members regularly recording ideas
Attribute listing
Developing a new idea by looking at the positives and negatives.
Big-dream approach
Developing a new idea by looking without constraints i.e think of the problem and its solutions I, thinking big. Every possibility should be recorded and investigated without regard to all the negatives.
Parameter- analysis
Developing a new idea by focusing on parameter identification and creative synthesis. Parameter identification involves analysis variables in the situation to determine their importance.
2.3.2 Opportunity Recognition
- Some entrepreneurs have the ability to recognize a business opportunity which is fundamental to the entrepreneurial process as well as growing business.
- A business opportunity represents a possibility for the entrepreneur to meet a large enough unsatisfied need that is worthwhile.
- The key to recognition of an opportunity lies in the knowledge ( education) and experience gained either personal or through work by both
- The prior knowledge is as a result of the combination of education and experience.
- The entrepreneurship needs to be aware of this knowledge and experience and have the desire to understand and make use of it.
- The other important factors in this process include
Entrepreneurship alertness
Entrepreneurial networks - Those entrepreneurs who have the ability to recognize meaningful business opportunities are in strategic position to successfully complete the planning and development process and successfully launch a new venture.
2.3.3 Add Opportunity Identification
The sources of new ideas
Some of the more frequently used sources of business ideas for entrepreneurs include.
- Consumers
Potential entrepreneurs not only pay attention to potential customers but also monitor their potential needs through allowing the customers to express their opinions. - Existing products and services
Through monitoring and evaluating competitive products and services. - Distribution channels
Contact with members of the distribution channels since they are familiar with the needs of the market and give suggestions of new products and consumer needs. - Federal government
Can be a source of a business idea through
1. The patent office which contains numerous product possibilities.
2. Official government magazines
3. Government regulatory bodies e.g KBS
4. Government shows and exhibitions
5. Research and development
Is the largest source of new ideas to the entrepreneur.
6. Education – i.e picking a given line of study e.g construction
7. Vocational training programmes and experience.
8. Personal hobbies especially for craft entrepreneurs.
9. Personal contacts and observations through. Interactions and Newspapers and magazines.
10. Conducting surveys and interviews of the people around.
11. Other ways of generating business ideas
2.3.4 Definition of a Business Opportunity
- A business opportunity may be defined as an attractive project idea with an entrepreneur accepts for investment on the basis of what is known about the possible success for the project
- A real business opportunity can by distinguish from a mere possibility through the following two ingredients.
A good market scope
An attractive return on investment ( profit)
2.3.5 Qualities (Characteristics) of a Good Business Opportunity
The following are qualities of a good business opportunity.
1. Demand – there should exist a good market scope
2. Returns on investment – i.e the business should be sufficiently profitable.
3. availability of raw materials
4. Enough skilled people.
2.3.6 Evaluation of Business Opportunities (objectives of a pre-feasibility study)
Once a business opportunity has been identified one needs to confirm that it is viable through a pre-feasibility study.
The main objective of a feasibility study is to determine whether.
1. the investment opportunity is promising enough
2. The project is viable from the marketing manufacturing and other points of view.
3. Any aspect of the project that may be crucial to call for indepth analysis.
2.3.7 The Purpose of Pre-feasibility Study (Market Research)
1. To verify that the investment opportunity is promising enough to make a firm decision.
2. To confirm that the project is viable from the
- Marketing
- Manufacturing and
- Other points of view
3. To identify any aspects of the project that is critical or crucial enough to call for in depth analysis
4. To acquire comprehensive technical, economic and commercial data for the final investment decision.
5. To enable an in-depth study of aspects such as
- Market potential
- Technical requirements
- Managerial ability
- Financial projections and analysis
- Risks evaluation
- Business environmental analysis.
To enable sourcing reliable information such as - Authorized publications
- Consultants openings.
6. To establish the final outcome of whether or not to proceed with the business.
2.4. Business Incubation
Business incubation is the process of nurturing small and start – up initiatives or business to relative maturity to become self-sustaining business, healthy and wealth-generating entities. The failure rate of any start-up business stands at 90% globally. The main causes of business
- Insufficient capital for start-up.
- Insufficient knowledge of business and industry.
- Lack of Entrepreneurial and business skills.
- Lack of Managerial skills.
- Inadequate Training.
- Lack of credit facilities.
- Lack of markets.
- Insufficient knowledge of markets.
- Inadequate infrastructure.
- Non-Empowering political environment.
For these reasons, many businesses which are ill-equipped do not survive. A business incubator is important for precisely those reasons above to provide these support services. Statistics show that the success rate for incubated businesses initiatives is very
high (over 80%) are bound to succeed.
2.4.1 The Incubation Process
- Help with business basics.
- Networking activities.
- Marketing assistance.
- Help with accounting and other financial management.
- Access to bank loans and other funds.
- Link to resource centers such as training institutions.
- Link to strategic partners.
- Help in the identification of a management team.
- Commercializing assistance.
The business incubation programmes are designed to accelerate successful development of entrepreneurial companies through an avvary of support resources and services. Incubators vary in the way they deliver their services in their organizational structure and in the types of clients they serve. Business incubators differ from research and technology in their dedication to start-up and early stage businesses. Research and Technology institutes tend to be large scale projects that house everything from corporate government or university labs to very small companies. The research institutions do not offer business assistance services which are the main objective of business incubation. Unlike many business assistance programmes business incubators do not serve any and all companies. Entrepreneurs who may wish to enter a business incubation program must apply for admission. Acceptance criteria vary from program to program but in general only those with feasible business ideas and workable business plan are admitted. The time a company spends in an incubation programme vary widely depending on a number of factors, including the type of business and the
Entrepreneur’s level of business Expertise.
2.4.2 The Benefits of Incubation.
- Creating jobs and wealth
- Fosters a community’s Entrepreneurial climate
- Technology commercialization.
- Diversification of Local Resource.
- Acceleration of local development.
- Facilitation of Business creation and growth.
- Encouraging entrepreneurship especially women.
- Revitalization of the community as a whole.
- Growth of Private Sector Investment.
- Increased Tax Revenue.
- Equitable Development.
2.4.3 Government Roles in Promoting Incubation
- Creation of an enabling environment through;
i. Purchasing consumer products.
ii. Support programmes financially of the incubation process. - Government policy to buy from incubators.
- Give small scale businesses loans and grants.
- Launch campaign to sensitize the private sector to work with business incubation initiative.
- Take a lead role in the incubation process.
- Assist in the coordination, encouraging and streamling the efforts of incubation at National level.
- Lobby and Rally with Kenyans in Diaspora together with developing partners to support business Incubation.
- To encourage coordination of independent efforts country-wide for better synergy and a more effective Natural impact
- To rally universities and other research institutions behind the concept to facilitate research and development in order to enrich business incubation
- To provide support to business incubation initiative by providing morale support through Media Initiatives.
2.4.4 Protections of Business ideas & maintaining Secrecy
Most entrepreneurs will not be inventors, at least not in the classic sense but all entrepreneurs are concerned with protecting their business ideas, especially when those ideas are related to; Un usual production and Unique designs et.c And for this to be done understand the “ patent law” becomes but simply paramount. When entrepreneurs want to protect unusual brand name, products business ideas or simply establishing ownership, then understanding trade marks and copyrights if vital as a way of protecting a business idea. The government law pertaining to;
- Patents
- Trademarks
- Copyrights – are not complicated
Many entrepreneurs file their own patent claims or prepare documentation for trademark or copyright protection without professional help from the Attorney or patent agents. However it is always wise to have professional assistance though the laws are simple.
2.4.5 Ways of Protecting Business ideas
A patent
A patent is a grant of property right by the government to an inventor. It is issued thought the commissioner of patent rights, and the most common type of patent is called a utility patent. All patent however, have the distinction of being assets with a commercial value because they provide exclusive rights of ownership the patent holders. Patents are exclusive property rights that can be sold, transferred, or used as collateral much alike other valueable assets. The patent law stipulates broad categories of what can and cannot be patented and in the words of the statute any person who “ invents or discovers any new and useful process, machine manufacture, or composition of matter, or ay new and useful improvements thereof may obtain a patent” Anything that is patentable must be new and useful ( must have some demonstrated function)
2.4.6 The Nature of Patentable Inventions
The terms used give classification of patentable
1. Process – The word process as used in patents refers to new methods of manufacturing or new technological procedures that can be validated as unique.
2. Machine – In patent law means that the patent application if for a specific physical item.
3. Manufacture- refers to physical items that have fabricated through new combinations of materials or technical applications.
The application must explain how the product is made including materials processes e.t.c.
4. Composition of Matter- this category is patent law relates to the chemical compounds such as synthetic materials, medicine, cosmetics etc
2.4.7 Types of Patents
Patent law provides for three categories of patents namely
- Utility patent
- Design patent
- Plant patent.
1. The utility patent
utility patent is granted for new products processes, machines, methods of manufacturing and composition of matter. This category excludes, most botanical creations related to plant and agricultural use.
2. The design patents
Are granted for any new or original ornamental design for an article of manufacture. A design patent protects the appearance of an article and not the article itself.
3. The plant patents
In botanical terms any, new variety of plant that have been sexually reproduced can be granted a plant patent. The new plant must not exist in nature or in an un cultivated state. Therefore new plants hybrids and seedlings may be patented.
4. Disclosures
- The patent office provides an important service of limited protection through the invention disclosure programme
- As a first step in seeking protection form the disclosure statement – the aim is to register an idea with the government.
- The investor explains what the items is, that it is new and useful and how it is to be used copy is given or photograph.
- This gives the investors protection as evidence of any legal tassel, or conflicting claims giving the investor priority.
2.4.8 The Patent Procedures
- The disclosure
When an idea is first reduced to sketches on paper or when it is mocked up, a disclosure should be filed. This is a measure of insurance that precedes the actual patent and provides legal recognition for all aspiring inventors. If someone took the sketches or steals the idea, evidence is on record. - The patent sketch
A patent sketch is required to determine whether an inventor’s creation already exists and remains actively protected under the law. - The preliminary section
The preliminary search scans the patent summaries for prior claims or invention. Records are accessed to make judgments and diligent decisions are made. - Collecting search documents
The application can the collect the approved documents for further processing. - Making the patent application
A formal application is now made at the search and is sent to the commissioner of patents and trade market
The application contains three parts
- A description of the item
- A set of drawings
- A formal oath or declaration
- Payment of patent filing ideas
2.4.9 Trademarks
Trademarks include any word, name, symbol or distinguishing device or any combination thereof adopted and used by a manufacturer or merchant to identify his goods and distinguish them from those manufactured or sold by others. Trade-marks can be names used in commerce such as KCA it can be a symbol or any distinguishing device artistic in nature. An important qualification for a trademark is that mark, name etc. must be used commercially.
2.4.10 Service mark Is similar to at trademark and can be registered in the same way
with the sale protection A service market can be a name, wording used in advertising symbols or artistic figures that create a distinctive service concept.
2.4.11 Copyrights
- Are similar to patents in establishing ownership and protection for creative ideas but they pertain to the intellectual property.
- The copyright is distinct from patents and trademarks in that intellectual property is protected for the life of the originator plus a further 50 years.
- This protection affords an extraordinary property right and substantial estates. It extends protection to author, composers and artists.
2.4.12 Trade Secrets
Are proprietary information used in the course of business to gain an advantage in manufacturing or commercialization of products or services.
Trade secrets
- formulas
- patterns
- list of customers
- data bases
- chemical compounds
- combinations of ingredients for commercial products
- process of manufacturing
- Complied information.
- Every organization must keep their secrets because
Modern communications systems contain so much information which if not guarded, the business may collapse.
Employees leaving may disseminate information to competitors.
In any business to maintain a market Niche, then desire to protect their product.
2.4.13 Trade Secrets
In certain instances the entrepreneur may prefer to maintain an idea or process as confidential, and eventually sell or license it as a trade secret. The trade secret will have a life as long as the idea or process remains secret. A trade secret in not covered by any law but is recognized under a governing body. Employees involved in working with an idea or process may be asked to first sign a confidential information agreement that will protect against their giving out the trade secret either while as employees or when leaving the organization – this is called trade secret non -disclosure agreement. Most entrepreneurs have limited resources so they choose not to find means of protecting their ideas or products or services.
2.4.14 Steps to be taken in order to maintain Secrecy in an Organization.
- Train employees to refer sensitive questions to designated personnel
- Provide proper security measures such as escorts to all visitors
- Avoid discussing business ideas in public places
- Keep important travel plans secret.
- Control information that might be presented by employees at conferences or published journals
- Use simple security measures such as locked file cabinets, passwords or computers, shedders e.t.c.
- Have employees and consultants sign non-disclosure agreements.
- Debrief departing employees on any confidential information.
- Avoid faxing any sensitive information
- Mark documents confidential when needed.
Unfortunately protection against the leaking to trade secrets is difficult to enforce.
2.4.15 Licensing
- Licensing may be defined as an agreement between two parties, where one party has proprietary rights over some information, process or technology protected by a patent, trademark or copyright.
- This arrangement specified in a contract requires the licence to pay royalty or some other specified sum to the holder of the proprietary rights in return for permission to copy the patent trade mark or copyright.
- Licensing has significance as a marketing strategy to holders of patents, trademarks or copyrights to grow their business in a new market when they lack resources or experiences in such markets.
- It is also an important marketing strategy for entrepreneurs who wish to start a new venture but need permission to a copy or incorporate the patent trademark or copyright with the ideas.
2.5. Product Safety and Liability
- It is very important for the entrepreneur to assess whether any product that is to be marketed in the new venture is subject to any regulations under the consumer product.
- In addition to setting standards for products the commission also has a great deal of responsibility and power to identify what to consider being a substantial hazard and barring any products that may be considered unsafe.
- Any products introduced by entrepreneurs must obtain clearance from the Kenya bureau of standards under the consumers protection Act.



